Gauss Law Integral Form
Gauss Law Integral Form - Web to get some more intuition on gauss' law, let's look at gauss' law in integral form. Web the new law follows an approach used in about a dozen states to require trial courts to conduct a meaningful review of the evidence before allowing a plaintiff to. ∫ e ⋅d a =q/ε 0. Web the integral of a gaussian function. What is the differential form of the gauss. This is known as gauss’s law in integral. The integral of an arbitrary gaussian function is. Gauss’s law states that the net electric flux through any hypothetical closed surface is equal to 1/ε 0 times the net electric charge within that closed surface. Web in missouri, many local governments, media outlets and others sources offer free services that automatically send out notifications alerting users to severe weather advisories,. Gauss’ law is one of the four fundamental laws of classical electromagnetics, collectively known as maxwell’s equations.
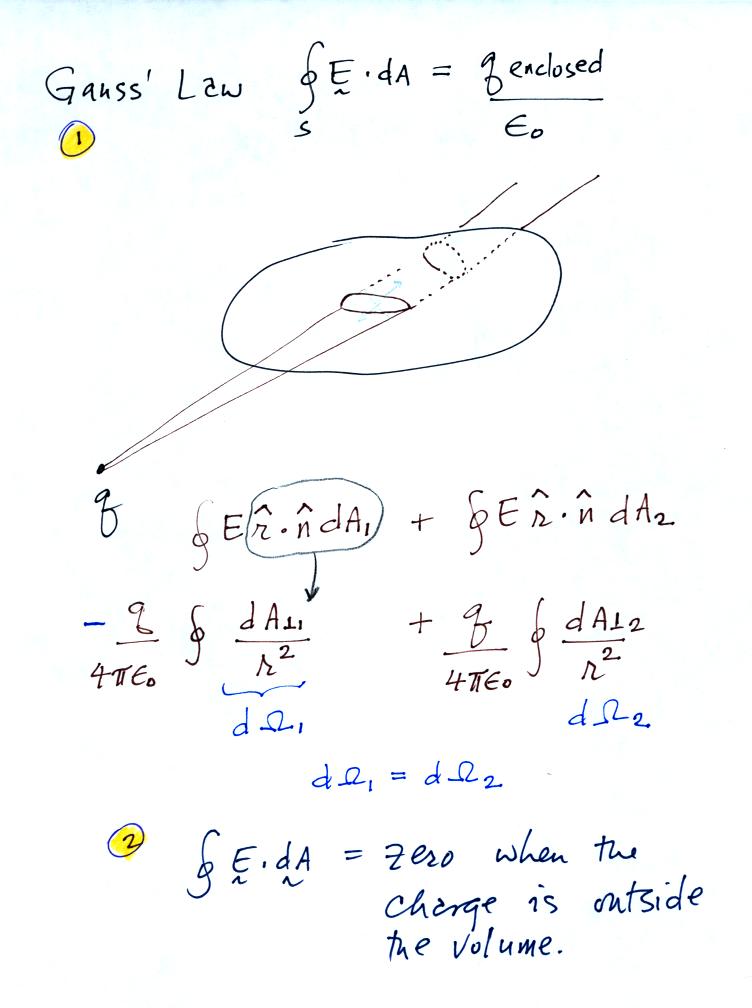
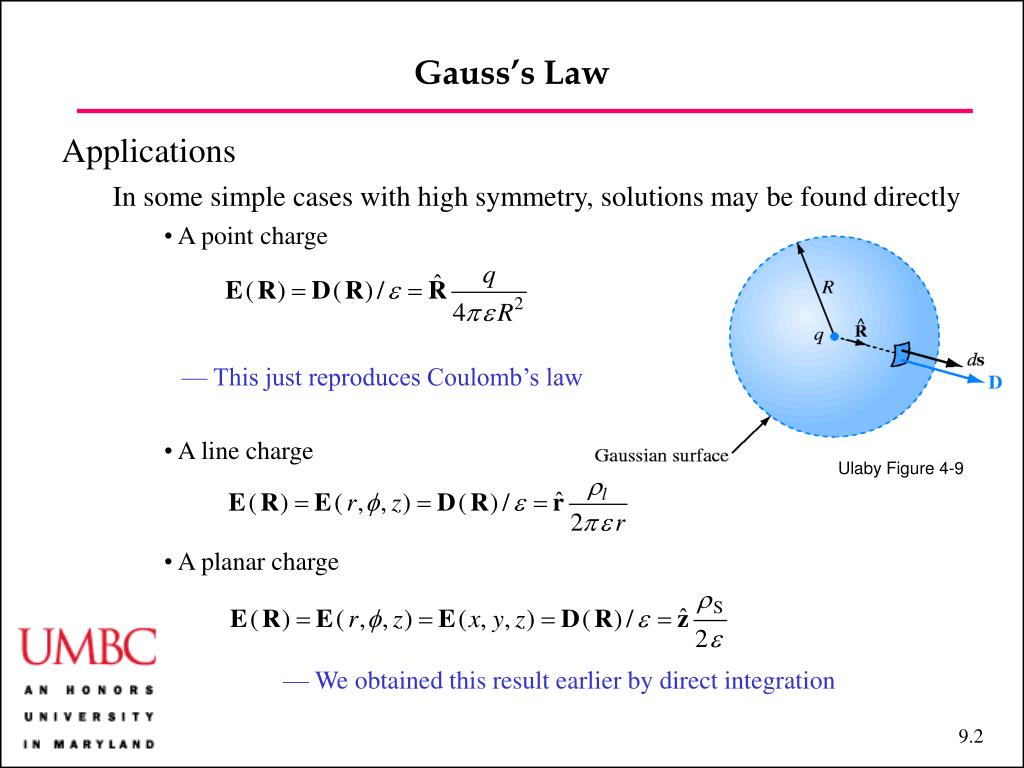
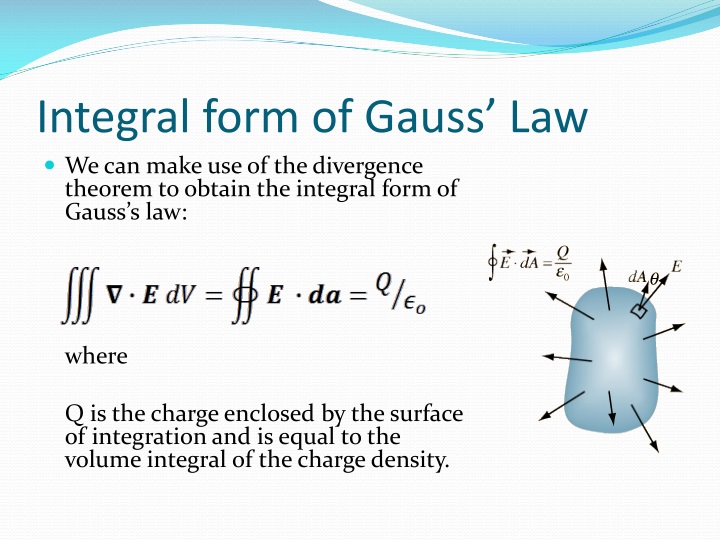
This relation or form of the gauss law is known as the integral form. Web this is the gauss law in the integral form. Web gauss’ law for magnetic fields (glm) is one of the four fundamental laws of classical electromagnetics, collectively known as maxwell’s equations. Web this equation has all the same physical implications as gauss' law. Gauss's law can be stated using either the electric field e or the electric displacement field d. Web there is another form of gauss’s law, known as the “integral form of gauss’s law.” this form of the law, shown in figure 5.7, considers not just a point in space, but an entire. Gauss’ law (equation 5.5.1) states that the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is equal to the enclosed. This is known as gauss’s law in integral. Web you are confusing work on a closed loop, with an integral on a closed surface. After all, we proved gauss' law by breaking down space into little cubes like this.
To do this, we assume some arbitrary volume (we'll call it v) which has a boundary (which is. What is the differential form of the gauss. The integral of an arbitrary gaussian function is. This form is useful for calculating expectations of some continuous. Web in missouri, many local governments, media outlets and others sources offer free services that automatically send out notifications alerting users to severe weather advisories,. The form with d is below, as are other forms with e. Web the new law follows an approach used in about a dozen states to require trial courts to conduct a meaningful review of the evidence before allowing a plaintiff to. Web you are confusing work on a closed loop, with an integral on a closed surface. After all, we proved gauss' law by breaking down space into little cubes like this. This section shows some of the forms with e;
Tue., Jan. 27 notes
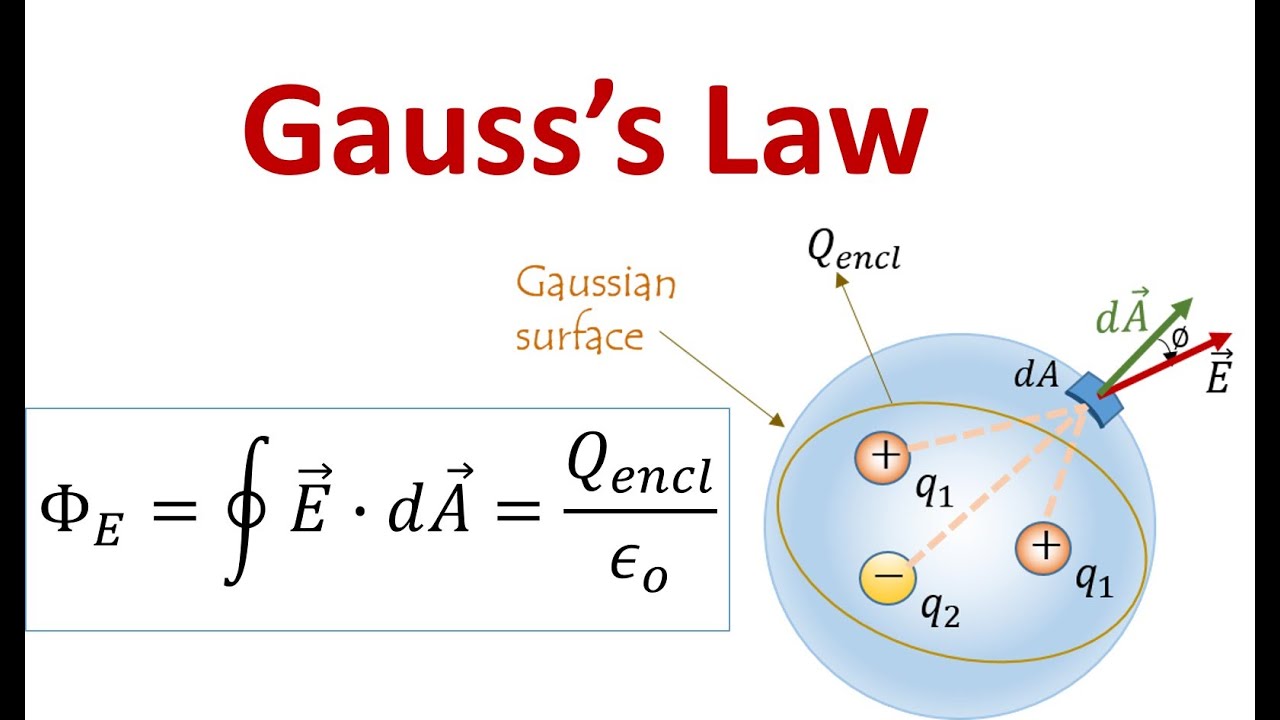
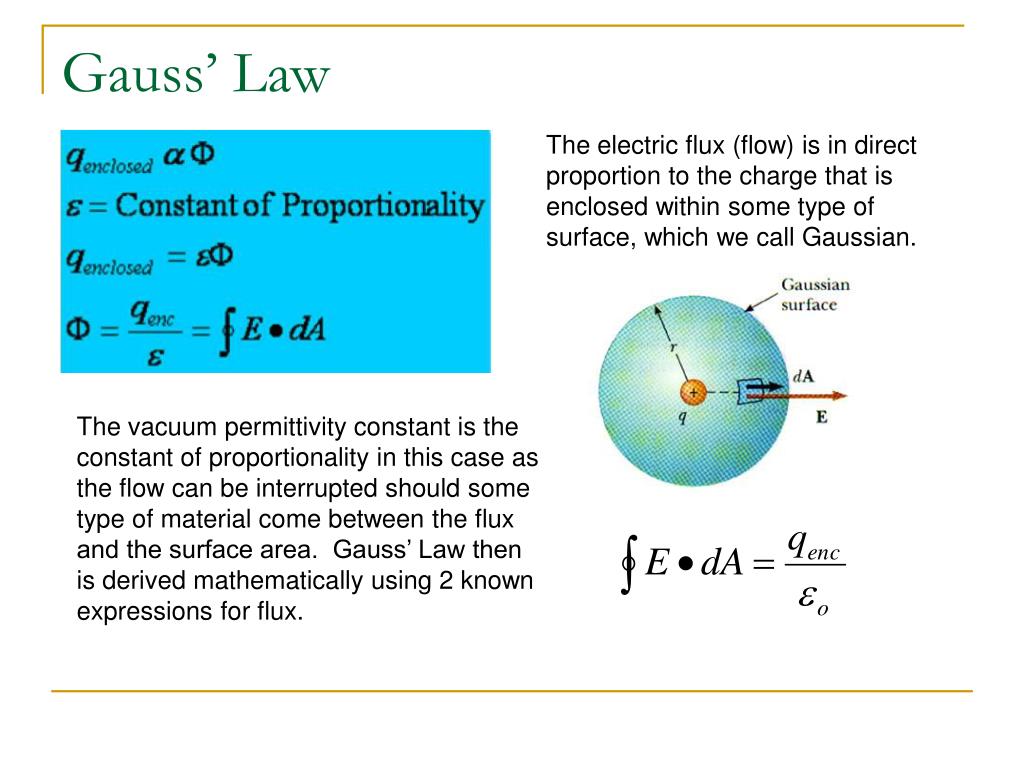
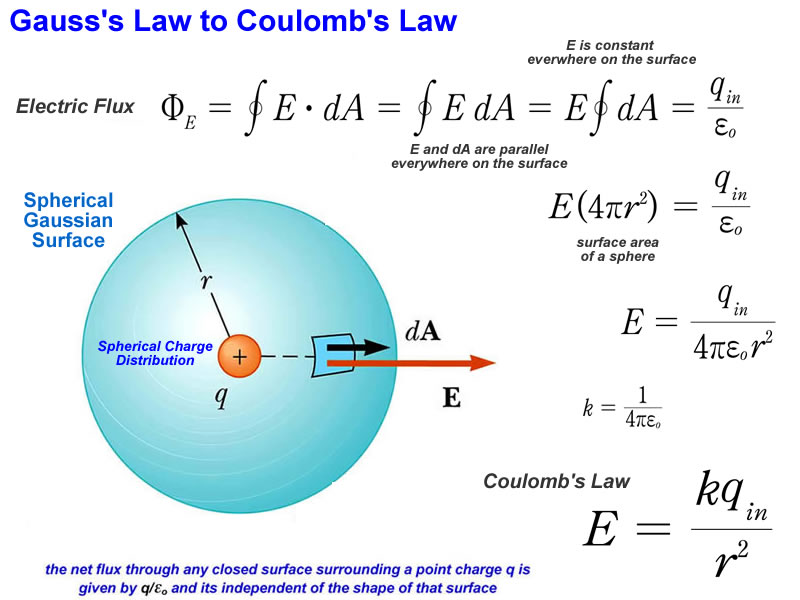
The area integral of the electric field over any closed surface is equal to the net charge enclosed in the surface divided by the permittivity of space. Gauss’s law in integral form is given below: Web notably, flux is considered an integral of the electric field. Coulomb's law is only true if. Web 1,520 2 19 35 7 while it's.
Gauss's Law and It's Applications YouTube
This relation or form of the gauss law is known as the integral form. Web the integral of a gaussian function. The form with d is below, as are other forms with e. Web let us now study gauss’s law through an integral equation. Web the new law follows an approach used in about a dozen states to require trial.
PPT Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1402148
Web gauss' law, integral form. Web the distance formula scalar fields vector fields the cross product 6 potentials due to discrete sources electrostatic and gravitational potentials and potential energies. Web the new law follows an approach used in about a dozen states to require trial courts to conduct a meaningful review of the evidence before allowing a plaintiff to. Gauss’s.
integral form of gauss's law Gauss's law, Law, Definitions
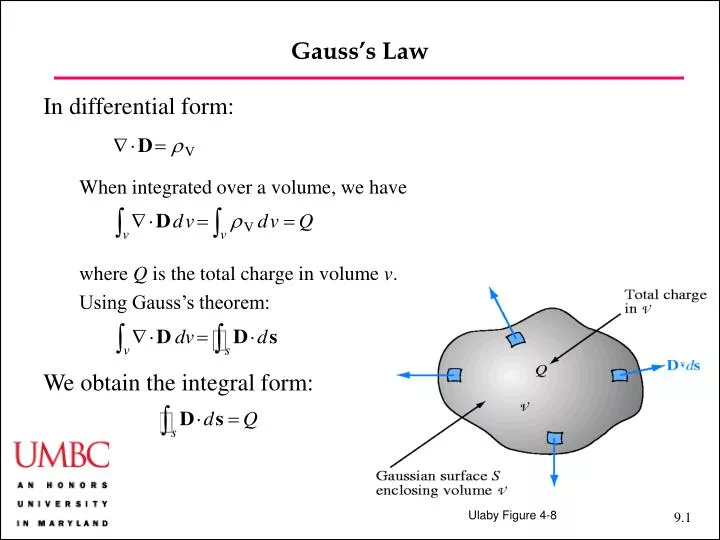
(1) where, e is the electric field vector q is the. Web the distance formula scalar fields vector fields the cross product 6 potentials due to discrete sources electrostatic and gravitational potentials and potential energies. Web gauss’s law in integral form. Coulomb's law is only true if. Web you are confusing work on a closed loop, with an integral on.
PPT3Gauss Law
To do this, we assume some arbitrary volume (we'll call it v) which has a boundary (which is. This relation or form of the gauss law is known as the integral form. Web let us now study gauss’s law through an integral equation. Missouri housing development commission attn: What is the differential form of the gauss.
PPT Gauss’ Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID301514
Web to get some more intuition on gauss' law, let's look at gauss' law in integral form. Web this is the gauss law in the integral form. The integral of an arbitrary gaussian function is. This is known as gauss’s law in integral. Gauss’ law is one of the four fundamental laws of classical electromagnetics, collectively known as maxwell’s equations.
Gauss's Law
Gauss’ law (equation 5.5.1) states that the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is equal to the enclosed. Web 1,520 2 19 35 7 while it's healthy to know these derivations, you should keep in mind that gauss's law is more general than coulomb's law. Web notably, flux is considered an integral of the electric field. This.
PPT EE3321 ELECTROMAGENTIC FIELD THEORY PowerPoint Presentation ID
Web there is another form of gauss’s law, known as the “integral form of gauss’s law.” this form of the law, shown in figure 5.7, considers not just a point in space, but an entire. Web the integral of a gaussian function. Web you are confusing work on a closed loop, with an integral on a closed surface. Gauss's law.
Gauss´s Law for Electrical Fields (integral form) Astronomy science
Web section 2.4 does not actually identify gauss’ law, but here it is: After all, we proved gauss' law by breaking down space into little cubes like this. (1) where, e is the electric field vector q is the. Gauss's law can be stated using either the electric field e or the electric displacement field d. What is true is.
PPT Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1402148
Web there is another form of gauss’s law, known as the “integral form of gauss’s law.” this form of the law, shown in figure 5.7, considers not just a point in space, but an entire. ∫ e ⋅d a =q/ε 0. Web section 2.4 does not actually identify gauss’ law, but here it is: Where q_enc is the total charge.
Web To Get Some More Intuition On Gauss' Law, Let's Look At Gauss' Law In Integral Form.
Where q_enc is the total charge enclosed by the closed surface we are integrating over. This is known as gauss’s law in integral. This section shows some of the forms with e; The area integral of the electric field over any closed surface is equal to the net charge enclosed in the surface divided by the permittivity of space.
Web You Are Confusing Work On A Closed Loop, With An Integral On A Closed Surface.
Web 1,520 2 19 35 7 while it's healthy to know these derivations, you should keep in mind that gauss's law is more general than coulomb's law. Web notably, flux is considered an integral of the electric field. Web of a witness or law enforcement as to the identity of the person who committed the offense. Gauss's law may be expressed as:
This Relation Or Form Of The Gauss Law Is Known As The Integral Form.
Web gauss’s law in integral form. Web in missouri, many local governments, media outlets and others sources offer free services that automatically send out notifications alerting users to severe weather advisories,. Web section 2.4 does not actually identify gauss’ law, but here it is: Gauss’ law is one of the four fundamental laws of classical electromagnetics, collectively known as maxwell’s equations.
Web This Is The Gauss Law In The Integral Form.
What is the differential form of the gauss. Web the distance formula scalar fields vector fields the cross product 6 potentials due to discrete sources electrostatic and gravitational potentials and potential energies. Gauss’s law states that the net electric flux through any hypothetical closed surface is equal to 1/ε 0 times the net electric charge within that closed surface. Web the integral of a gaussian function.