What Types Of Atoms Form Covalent Bonds
What Types Of Atoms Form Covalent Bonds - When atoms of different elements share electrons through covalent bonding, the electron will be drawn more toward the atom with the higher e lectronegativity resulting in a polar covalent bond. A type of chemical bond where two atoms are connected to each other by the sharing of two or more electrons. Web formation of covalent bonds. Web double bonds triple bond. Living things are made up of atoms, but in most cases, those atoms aren’t just floating around individually. Web there are actually three different types of chemical bonds, called covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds. Illustrates why this bond is formed. In organic chemistry, when a molecule with a planar ring obeys hückel's rule, where the number of π electrons fit the formula 4 n + 2. Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron. Various methods of showing a covalent bond.
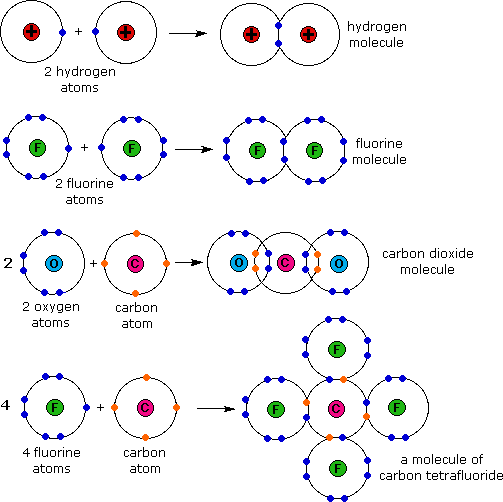
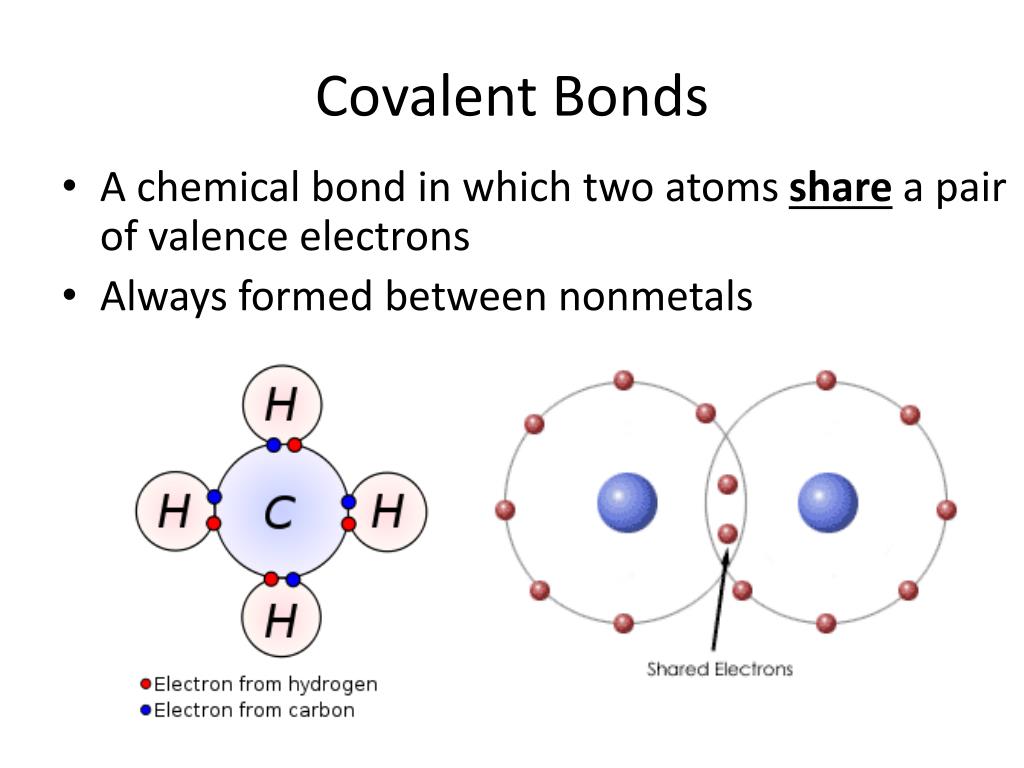
Web the shorter bond length has greater bond strength. Positively charged and negatively charged parts of covalent molecules attract c. This type of covalent bond is. Living things are made up of atoms, but in most cases, those atoms aren’t just floating around individually. The simplest covalent bond exists in the diatomic hydrogen molecule. Web molecular shape isomerism in organic compounds there are many types of chemical bonds and forces that bind molecules together. Various methods of showing a covalent bond. Web when electrons are shared between two atoms, they form a covalent bond. Each atom contributes one electron to the shared pair, helping both atoms achieve an octet in their valence shell. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms.
What is a covalent bond? Web when electrons are shared between two atoms, they form a covalent bond. Each h atom starts with a single electron in its valence shell: Molecules of identical atoms, such as h 2 and buckminsterfullerene (c 60 ), are also held together by covalent bonds. Covalent bonds form between atoms of nonmetallic elements. Positively charged and negatively charged parts of covalent molecules attract c. Based on the bond length, covalent bonds are of the following types. Web introduction only when two atoms of the same element form a covalent bond are the shared electrons actually shared equally between the atoms. How does that work in. Web nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms.
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
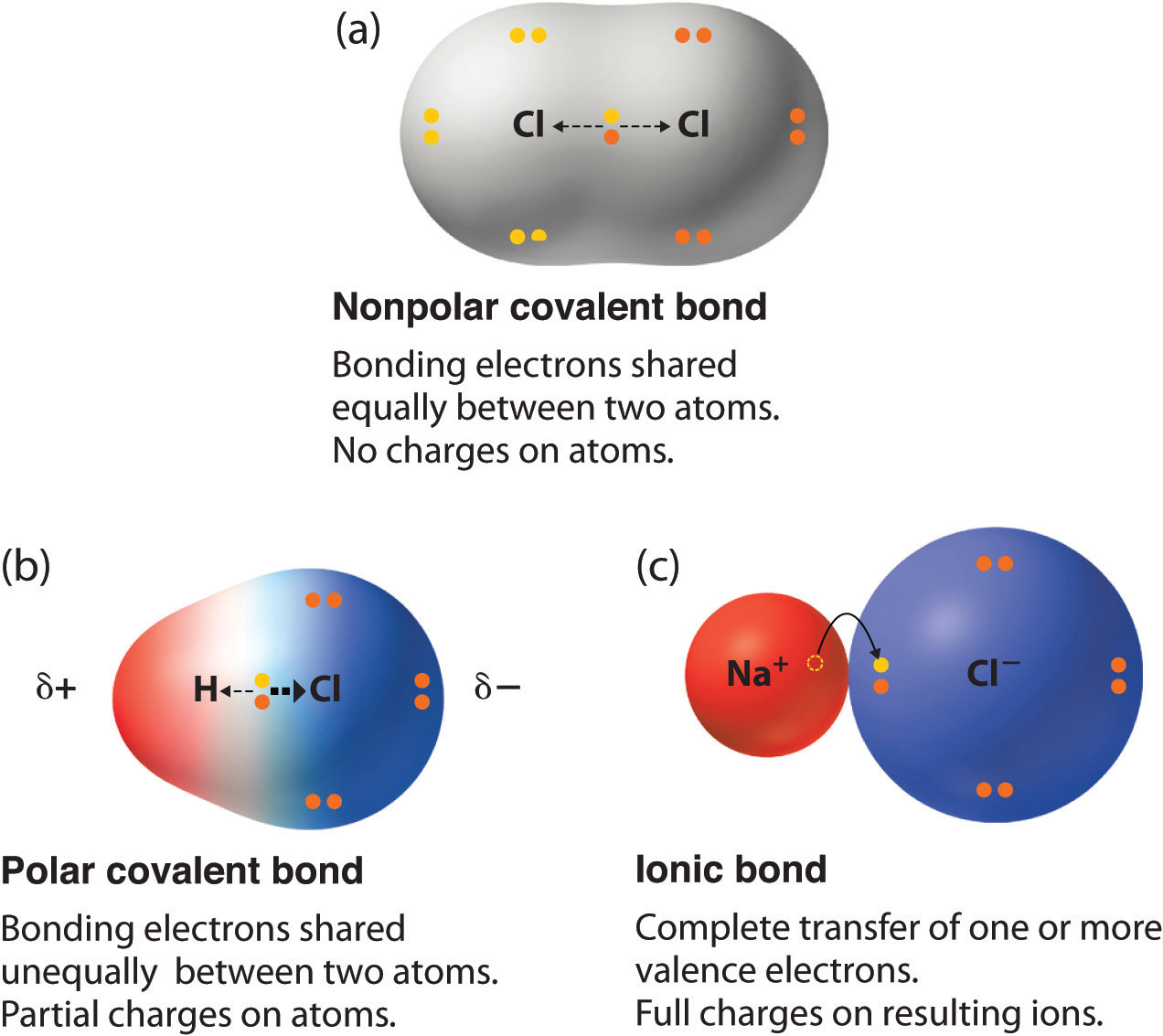
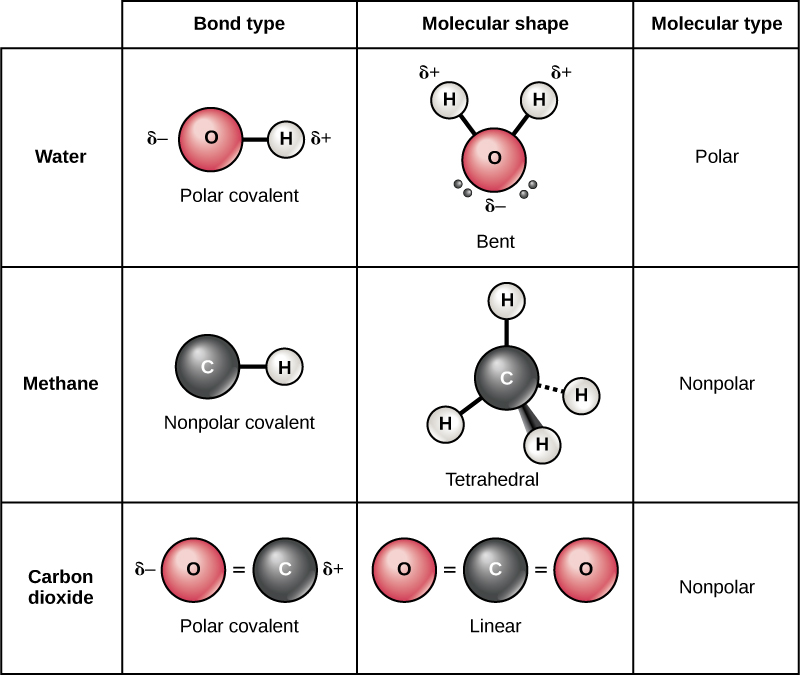
Web there are two main types of covalent bonds that can occur based on the electronegativity of the atoms involved: Positively charged and negatively charged parts of covalent molecules attract c. This type of covalent bond exists where the unequal sharing of electrons occurs due to the. Web a covalent bond is formed when electrons from both participating atoms are.
EduMission Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 5 Covalent Bond
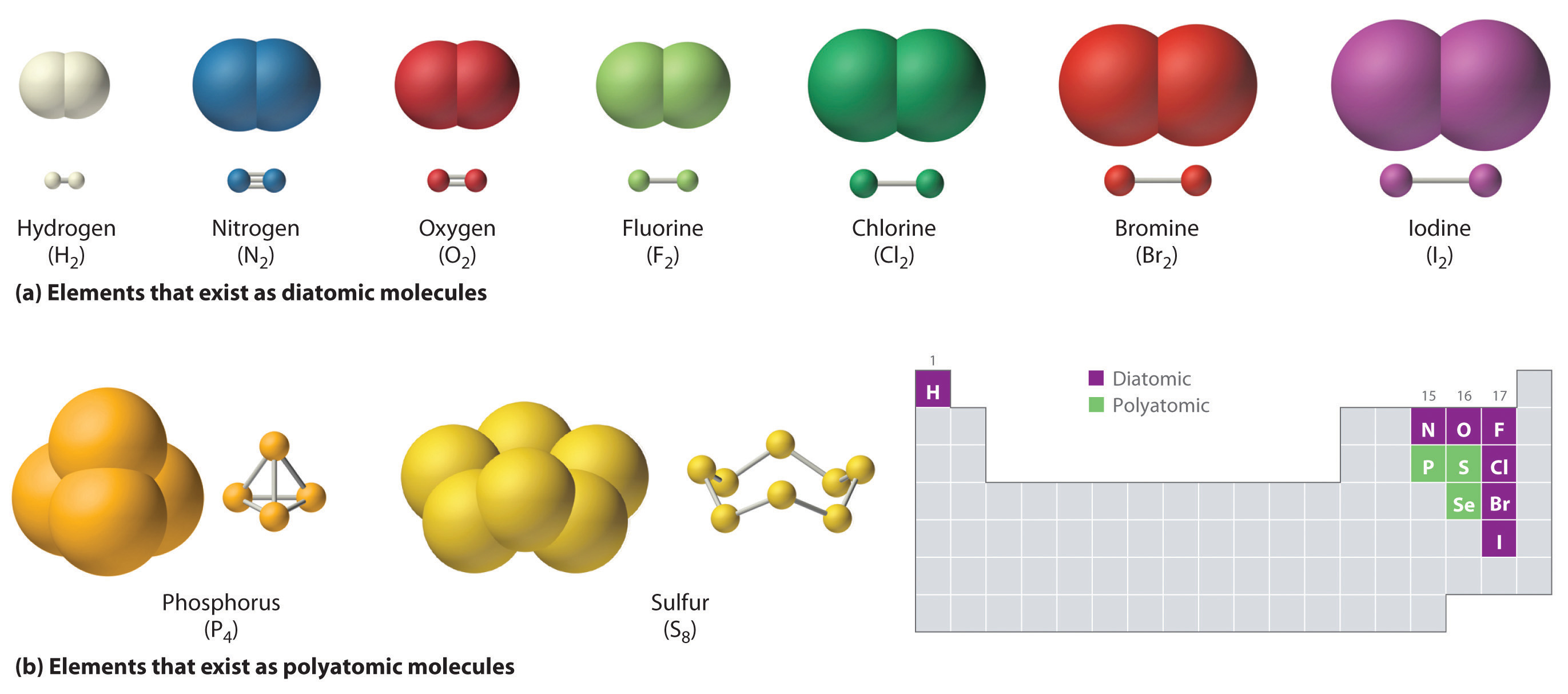
Halogens also exist as diatomic gases by forming covalent bonds, such as chlorine. What is a covalent bond? A covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two nonmetal atoms that share a pair of electrons. Each h atom starts with a single electron in its valence shell: A type of chemical bond where two atoms are connected.
Polar Covalent Bonds
Single covalent bonds between different atoms. In lewis theory, a pair of electrons, known as a bonding pair, is shared between two atoms to form a covalent bond. Molecules of identical atoms, such as h 2 and buckminsterfullerene (c 60 ), are also held together by covalent bonds. Do a covalent bond should necessarily have a difference in their electronegativities..
covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
Web there are two main types of covalent bonds that can occur based on the electronegativity of the atoms involved: This type of covalent bond exists where the unequal sharing of electrons occurs due to the. An example of a covalent compound is ammonia. Web the shorter bond length has greater bond strength. Starting on the far right, we have.
PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183
In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Molecular bonds are another name for covalent bonds. A covalent bond forms when_______________. Covalent bonds form between atoms of nonmetallic elements. What types of atoms tend to form the following types of.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
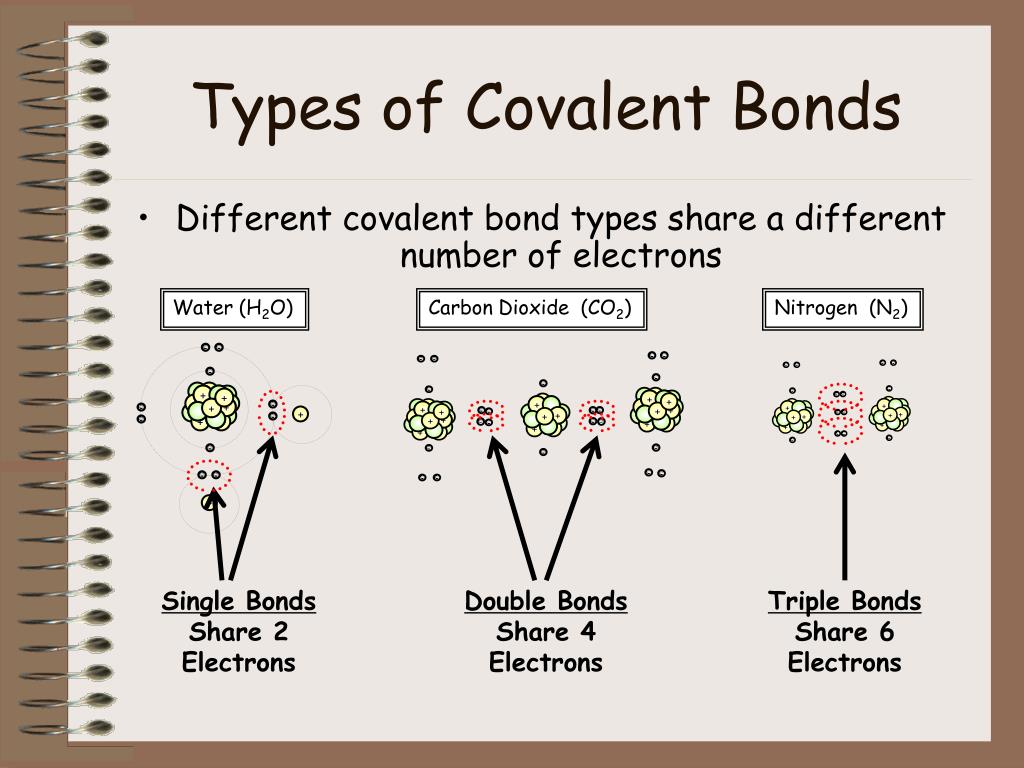
Web the two atoms can also share two pairs of electrons (a double bond) or three pairs of electrons (triple bond): A covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two nonmetal atoms that share a pair of electrons. Ionic bonds require at least one electron donor and one electron. Web as a general rule, covalent bonds are.
Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary
Web the shorter bond length has greater bond strength. Single covalent bonds between different atoms. Web the two atoms can also share two pairs of electrons (a double bond) or three pairs of electrons (triple bond): A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. Web chemistry biology robotics coding covalent bond.
PPT Notes 53 Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The differences between ionic and covalent bonds are explained by the use of scientific models and examples from nature. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2, contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. This type of covalent bond is. How does that work in. Living things are made up of atoms, but in most cases, those atoms aren’t.
Covalent Bonds Biology for NonMajors I
A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. A covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two nonmetal atoms that share a pair of electrons. The sharing of bonding pairs will ensure that the atoms achieve stability in their outer shell, similar. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent.
Covalent Enseñanza de química, Enlace químico, Enlace covalente
Web covalent bonds form between atoms with relatively high electron affinity and they form individual, separate molecules (figure below). When atoms of different elements share electrons through covalent bonding, the electron will be drawn more toward the atom with the higher e lectronegativity resulting in a polar covalent bond. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2, contains a covalent bond.
This Type Of Covalent Bond Exists Where The Unequal Sharing Of Electrons Occurs Due To The.
Web molecular shape isomerism in organic compounds there are many types of chemical bonds and forces that bind molecules together. In general, bonds are considered to be covalent if the electronegativity difference between the two atoms bonding is less than 2.0 pauling units. In lewis theory, a pair of electrons, known as a bonding pair, is shared between two atoms to form a covalent bond. Single covalent bonds between different atoms.
How Does A Covalent Bond Form?
Figure 7.4 illustrates why this bond is formed. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Starting on the far right, we have two separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy, indicated. Halogens also exist as diatomic gases by forming covalent bonds, such as chlorine.
Nonmetal Atoms Frequently Form Covalent Bonds With Other Nonmetal Atoms.
Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. Web double bonds triple bond. This type of covalent bond is. In organic chemistry, when a molecule with a planar ring obeys hückel's rule, where the number of π electrons fit the formula 4 n + 2.
Web As A General Rule, Covalent Bonds Are Formed Between Elements Lying Toward The Right In The Periodic Table (I.e., The Nonmetals).
Web covalent bonds form between atoms with relatively high electron affinity and they form individual, separate molecules (figure below). Web what types of atoms form covalent bonds? A covalent bond forms when_______________. Molecular bonds are another name for covalent bonds.