What Two Substances Form From An Acid Base Neutralization
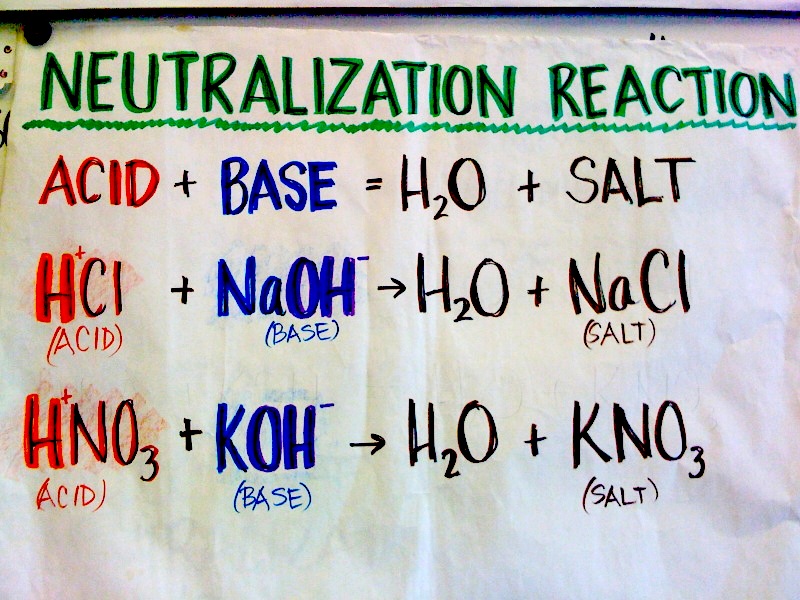
What Two Substances Form From An Acid Base Neutralization - Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s. Web answer (1 of 6): Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other's. The name of the salt. Reaction involving the transfer of a hydrogen ion between reactant species. Substance that produces h 3 o + when dissolved in water. Web in the context of a chemical reaction the term neutralization is used for a reaction between an acid and a base or alkali. Web a hydrogen ion is a hydrogen atom that has been stripped of its electron, resulting in a net positive charge: Web an acid base neutralization reaction is when an acid reacts with a base to create water and a salt. Acid + base → h 2 o + salt example 1:
Historically, this reaction was represented as acid + base. Web reaction of acids with metal carbonates and bicarbonates. Web the reaction of an acid and a base is called a. Web the reaction of an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction. Web answer (1 of 6): Sodium bicarbonate is i think the best practical answer to this question. Web reactions between strong acids and strong bases decompose more completely into hydrogen ions (protons, positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions) in. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other's. Web a reaction between an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction and can be represented as: Web an acid base neutralization reaction is when an acid reacts with a base to create water and a salt.
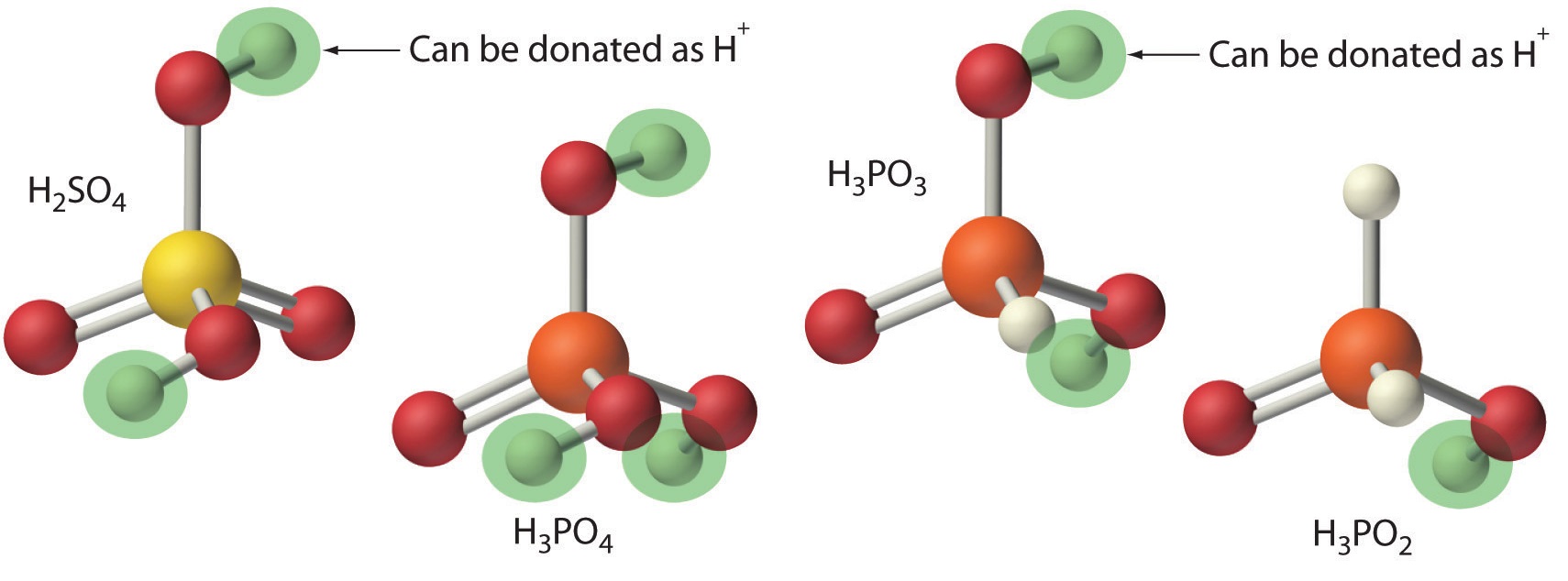
The name of the salt. Acid + base → h 2 o + salt example 1: The arrhenius definition states that an acid produces h + in solution and a base. Web there are three major classifications of substances known as acids or bases. Web chemistry acids and alkalis key points an acid and alkali will neutralise each other and produce a salt and water. Substance that produces h 3 o + when dissolved in water. Reaction involving the transfer of a hydrogen ion between reactant species. Web according to brønsted and lowry, an acid (a substance with at least one hydrogen atom that can dissociate to form an anion and an \(h^+\) ion (a proton) in. Web a hydrogen ion is a hydrogen atom that has been stripped of its electron, resulting in a net positive charge: Web reaction of acids with metal carbonates and bicarbonates.
Acids and Bases Lemon Juice and Toothpaste Neutralization
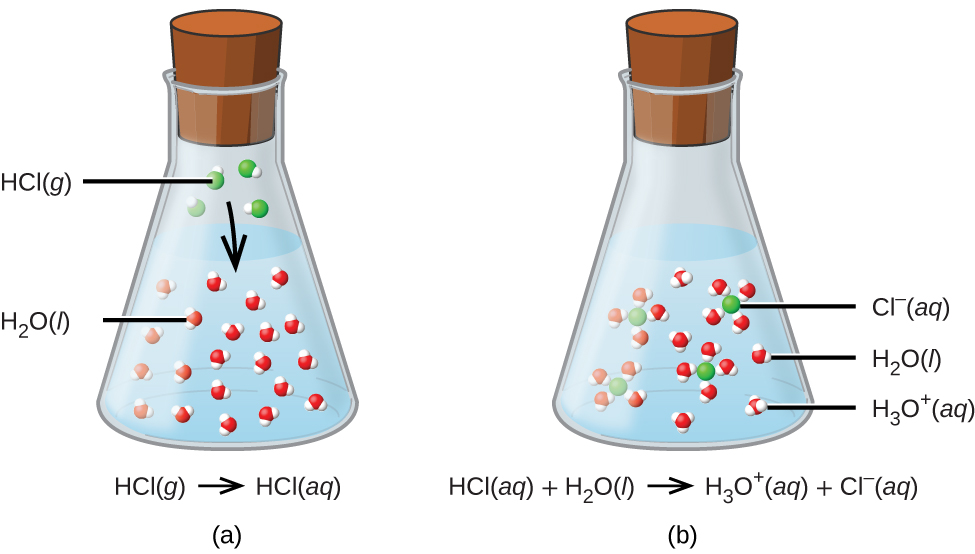
As an example, consider the equation shown here: Web a hydrogen ion is a hydrogen atom that has been stripped of its electron, resulting in a net positive charge: Web the reaction of an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s. Reaction.
Acid Base Neutralization Equation YouTube
Web an acid base neutralization reaction is when an acid reacts with a base to create water and a salt. Web a hydrogen ion is a hydrogen atom that has been stripped of its electron, resulting in a net positive charge: Web there are three major classifications of substances known as acids or bases. Basic substances neutralise acids, resulting in.
Spice of Lyfe Neutralization Chemical Reaction
The name of the salt. This is called a neutralisation reaction. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s. Web chemistry acids and alkalis key points an acid and alkali will neutralise each other and produce a salt and water. Historically, this reaction was represented as acid + base.
Is Na3PO4 an acid or base or neutral
Web as observed, the acid and base reaction produced salt and water from the reactants that exchange cations and anions similar to a double displacement reaction. Web chemistry acids and alkalis key points an acid and alkali will neutralise each other and produce a salt and water. Substance that produces h 3 o + when dissolved in water. Because a.
Titration and AcidBase Neutralization online presentation
Reaction involving the transfer of a hydrogen ion between reactant species. Because a proton is identical to a hydrogen ion,. Web as observed, the acid and base reaction produced salt and water from the reactants that exchange cations and anions similar to a double displacement reaction. Historically, this reaction was represented as acid + base. Web according to brønsted and.
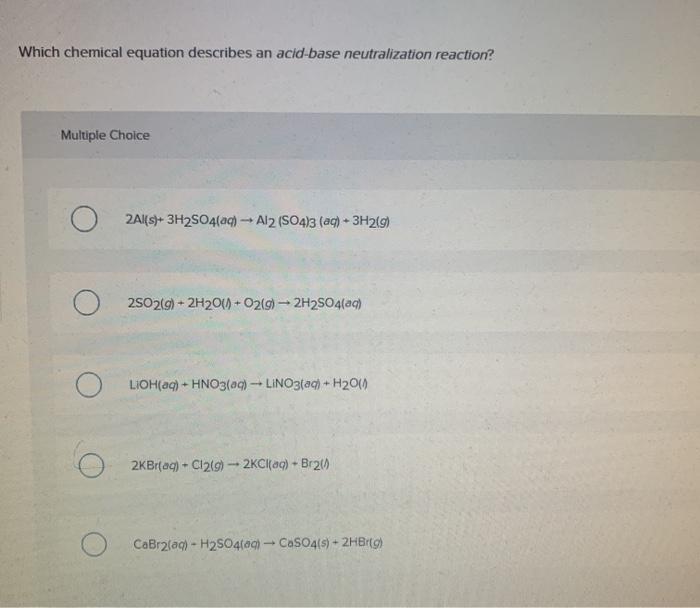
Solved Which chemical equation describes an acidbase
Web the reaction of an acid and a base is called a. Web according to brønsted and lowry, an acid (a substance with at least one hydrogen atom that can dissociate to form an anion and an \(h^+\) ion (a proton) in. Historically, this reaction was represented as acid + base. Web reaction of acids with metal carbonates and bicarbonates..
Class 10th Neutralization reaction and chemical properties of Acid and
Web a reaction between an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction and can be represented as: The arrhenius definition states that an acid produces h + in solution and a base. Web answer (1 of 6): Web an acid base neutralization reaction is when an acid reacts with a base to create water and a salt. Reaction.
Acid Base Neutralization Reactions & Net Ionic Equations Chemistry
Web a reaction between an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction and can be represented as: Web an acid base neutralization reaction is when an acid reacts with a base to create water and a salt. Substance that produces h 3 o + when dissolved in water. Web answer (1 of 6): This is called a neutralisation.
Acids and Bases 9 Properties, Useful Reaction & Examples
Substance that produces h 3 o + when dissolved in water. Web in this context, an acid is a substance that will dissolve in water to yield hydronium ions, h 3 o +. Because a proton is identical to a hydrogen ion,. Web metal oxides and alkalis are two types of base. Web chemistry acids and alkalis key points an.
Acids, Bases, Neutralization, and GasForming Reactions (M3Q34) UW
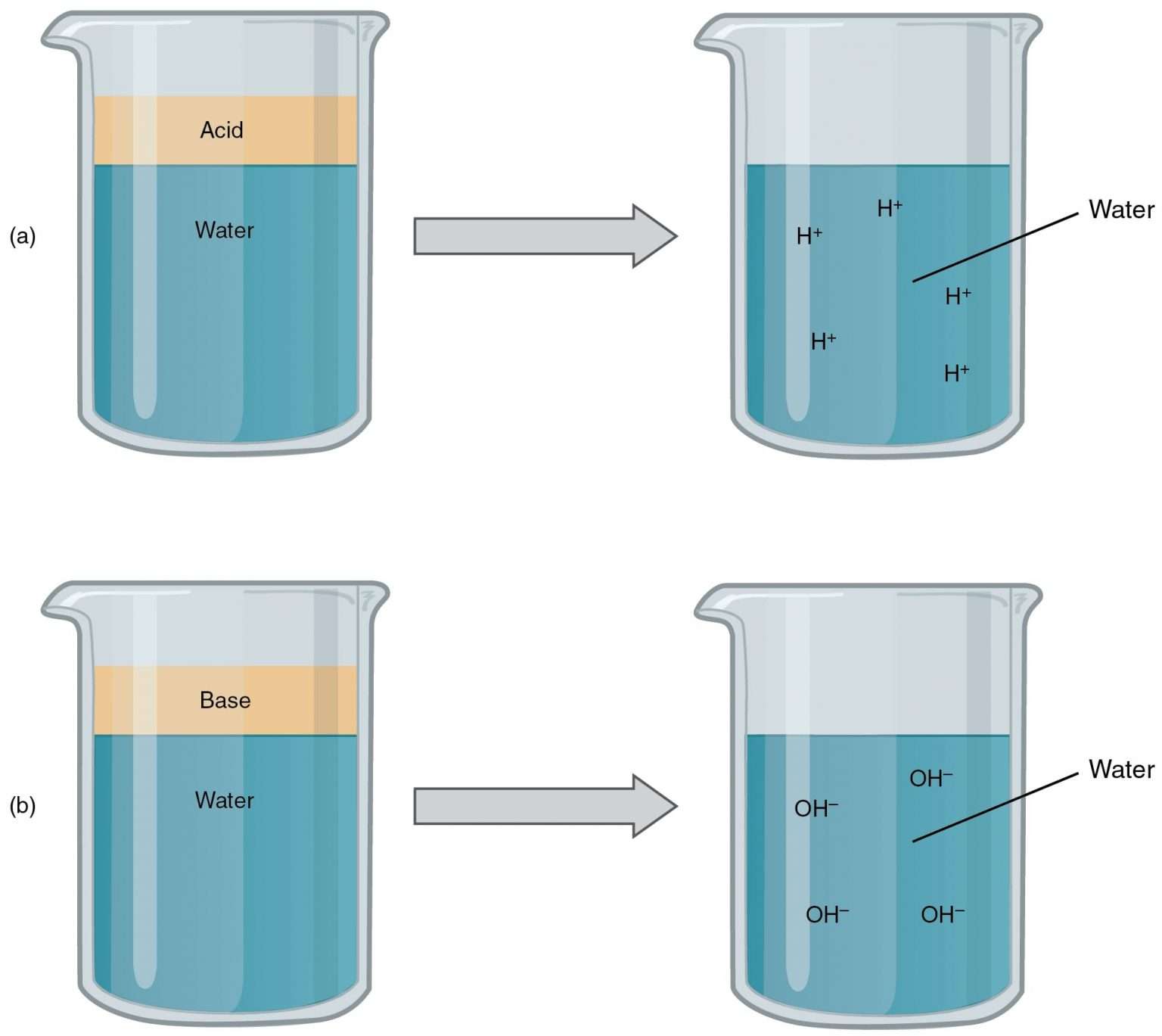
Web a hydrogen ion is a hydrogen atom that has been stripped of its electron, resulting in a net positive charge: Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s. The name of the salt. This is called a neutralisation reaction. Web reactions between strong acids and strong bases decompose more completely into.
Web In The Context Of A Chemical Reaction The Term Neutralization Is Used For A Reaction Between An Acid And A Base Or Alkali.
Sodium bicarbonate is i think the best practical answer to this question. Web a reaction between an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction and can be represented as: As an example, consider the equation shown here: Basic substances neutralise acids, resulting in the ph of the acid increasing towards 7, and water being produced.
The Name Of The Salt.
This is called a neutralisation reaction. Web metal oxides and alkalis are two types of base. Web as observed, the acid and base reaction produced salt and water from the reactants that exchange cations and anions similar to a double displacement reaction. Because a proton is identical to a hydrogen ion,.
Although Acids And Bases Have Their Own Unique Chemistries, The Acid And Base Cancel Each Other’s.
Substance that produces h 3 o + when dissolved in water. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other's. Web in this context, an acid is a substance that will dissolve in water to yield hydronium ions, h 3 o +. Web the reaction of an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction.
Web A Hydrogen Ion Is A Hydrogen Atom That Has Been Stripped Of Its Electron, Resulting In A Net Positive Charge:
The arrhenius definition states that an acid produces h + in solution and a base. Web there are three major classifications of substances known as acids or bases. Web chemistry acids and alkalis key points an acid and alkali will neutralise each other and produce a salt and water. Web reactions between strong acids and strong bases decompose more completely into hydrogen ions (protons, positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions) in.