The Recapitulation In Sonata Form
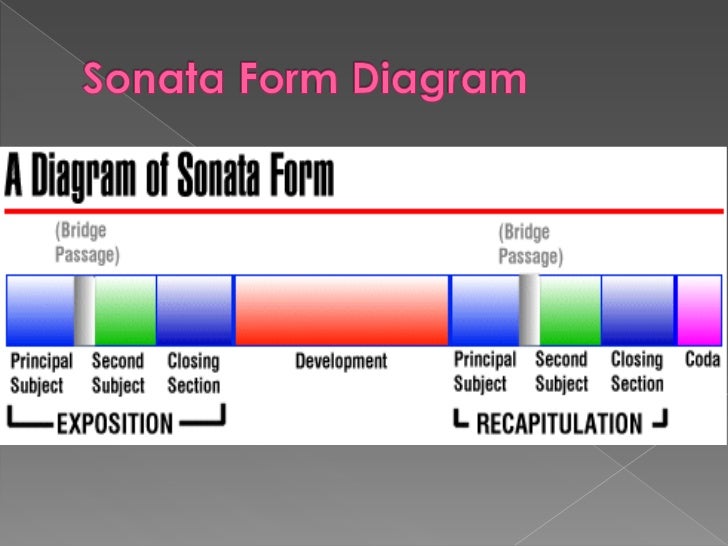
The Recapitulation In Sonata Form - The exposition has two core sections in different keys called the primary theme and secondary theme. Like its name implies, it is basically a restatement (or recap) of the main themes that were first presented in the exposition, except this time there is no transition to the v (or iii in minor). This form is commonly used in the first movement of sonatas, string quartets, symphonies and even concerts. An exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. The exposition the exposition has 2 themes (called subjects). It has three main sections: The primary and secondary themes are separated by a transition. A sonata may begin with an introduction, which is commonly slower than the remainder of the movement. Web the final section of a piece in sonata form is the recapitulation. The development and recapitulation may have a retransition between them.
An exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. Web sonata for piano alt ernative. The secondary theme is typically followed by a large suffix called the closing section. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early classical period ). Sometimes composer do that, but other times it will be used as a compositional challenge. The exposition has two core sections in different keys called the primary theme and secondary theme. The primary and secondary themes are separated by a transition. Like its name implies, it is basically a restatement (or recap) of the main themes that were first presented in the exposition, except this time there is no transition to the v (or iii in minor). Web the entire sonata form, therefore, is understood as a dynamic trajectory toward the esc, the basic plan of which is foreshadowed by the exposition's approach to the eec. First, it presents the main thematic material of the piece, and second, it modulates away from the home key.
The recapitulation is a varied repetition of the exposition. The secondary theme is typically followed by a large suffix called the closing section. An exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. The development and recapitulation may have a retransition between them. Sometimes composer do that, but other times it will be used as a compositional challenge. The second a section, or recapitulation. As for legroom, it provides 45.5 inches in the front and 35.6 inches in the back. The themes the composer introduced in the exposition are played again, often with some variation. The most important difference is that the second. The exposition has two core sections in different keys called the primary theme and secondary theme.
Sonata Form Part 4 Recapitulation YouTube
The exposition the exposition has 2 themes (called subjects). The exposition moves from the original key to a new key; Web the final section of a piece in sonata form is the recapitulation. And its trunk space is 16.3 cubic feet. The recapitulation occurs after the movement's development section, and typically presents once more the musical themes from the movement's.
Sonata Form The Recapitulation YouTube
The second a section, or recapitulation. Beethoven's 'pastorale' sounds like a brookside daydream, but. A musical form that consists basically of an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation and that is used especially for the first movement of a sonata example sentences recent examples on the web to these older materials, however, the work adds more adventurous harmonies and stretches.
Sonata Form Beginner's Guide Featuring Mozart K545
As for legroom, it provides 45.5 inches in the front and 35.6 inches in the back. The secondary theme is typically followed by a large suffix called the closing section. Web the harmonic goal of the recapitulation (and the sonata movement as a whole) is the essential sonata closure (esc). Web the final section of a piece in sonata form.
sonata_form_recap_keynote.001.jpg
Web the final section of a piece in sonata form is the recapitulation. Web the sonata form is probably one of the most common forms in classical and romantic music. It marks the end of the main argument and the beginning of the final synthesis for…. The second section then begins with some contrasting material in the secondary key. The.
Sonata form
Melbourne main street wins three state preservation awards Web the harmonic goal of the recapitulation (and the sonata movement as a whole) is the essential sonata closure (esc). After that, there is an exposition, whose purpose is to present the movement's main thematic material. Web the sonata has 40.4 inches of headroom in the front and 38 inches in the.
In sonata form, the exposition and recapitulation
The themes the composer introduced in the exposition are played again, often with some variation. 14 minutes composer time period comp. In theory, one could write the primary group with no transposition, and then transpose everything from the secondary group onwards into the tonic; It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early classical period.
Pin on Music
The exposition has two core sections in different keys called the primary theme and secondary theme. Sometimes composer do that, but other times it will be used as a compositional challenge. It has three main sections: The second a section, or recapitulation. This form is commonly used in the first movement of sonatas, string quartets, symphonies and even concerts.
WenatcheeTheHatchet Matiegka Grand Sonata I, recapitulation
As for legroom, it provides 45.5 inches in the front and 35.6 inches in the back. The primary and secondary themes are separated by a transition. The b section is called the development section, because it manipulates — or “develops” — the musical materials of the exposition. Recapitulation resulting from a bifocal close in the exposition. Web in music theory,.
[Solved] Question 11 (1 point) The recapitulation in sonata form (A
The primary and secondary themes are separated by a transition. The second section then begins with some contrasting material in the secondary key. Scherzo year/date of composition y/d of comp. A sonata may begin with an introduction, which is commonly slower than the remainder of the movement. The primary and secondary themes are separated by a transition.
Sonata form
The primary and secondary themes are separated by a transition. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early classical period ). Web the first a section of sonata allegro form is referred to by musicologists as the exposition section, because it states — or “exposes” — the thematic material. Scherzo year/date of composition y/d.
This Form Is Commonly Used In The First Movement Of Sonatas, String Quartets, Symphonies And Even Concerts.
14 minutes composer time period comp. An exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. Beethoven's 'pastorale' sounds like a brookside daydream, but. First, it presents the main thematic material of the piece, and second, it modulates away from the home key.
It Marks The End Of The Main Argument And The Beginning Of The Final Synthesis For Which That Argument Has Prepared The Listener’s Mind.
Scherzo year/date of composition y/d of comp. The crux is the part of the recapitulation where the. And its trunk space is 16.3 cubic feet. The development passes through several keys and the.
It Marks The End Of The Main Argument And The Beginning Of The Final Synthesis For….
Web the harmonic goal of the recapitulation (and the sonata movement as a whole) is the essential sonata closure (esc). The secondary theme is typically followed by a large suffix called the closing section. The b section is called the development section, because it manipulates — or “develops” — the musical materials of the exposition. In theory, one could write the primary group with no transposition, and then transpose everything from the secondary group onwards into the tonic;
The Second A Section, Or Recapitulation.
Web mozart preferred strongly differentiated themes, and he often reshaped his second subjects drastically when they reappeared in the recapitulation. Web the first a section of sonata allegro form is referred to by musicologists as the exposition section, because it states — or “exposes” — the thematic material. Like its name implies, it is basically a restatement (or recap) of the main themes that were first presented in the exposition, except this time there is no transition to the v (or iii in minor). The primary and secondary themes are separated by a transition.