The Axons Of Ganglion Cells Converge To Form
The Axons Of Ganglion Cells Converge To Form - The axons of ganglion cells. Brain (thalamus) where this nerve leaves the eye, there are no receptors; Web retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that. Thus, the area is called the ___ ___. Rods and cones are sensory neurons in our retina which provide our brains with the sensory inputs to help us. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form the ___ ___, which carries the visual information to the ___ bipolar; This nerve helps in the. Web introduction ganglion cellsare the projection neurons of the vertebrate retina, conveying information from other retinal neurons to the rest of the brain. While both major classes of ganglion cells (b cells and c cells) had. The axons of ganglion cells converge to form the.
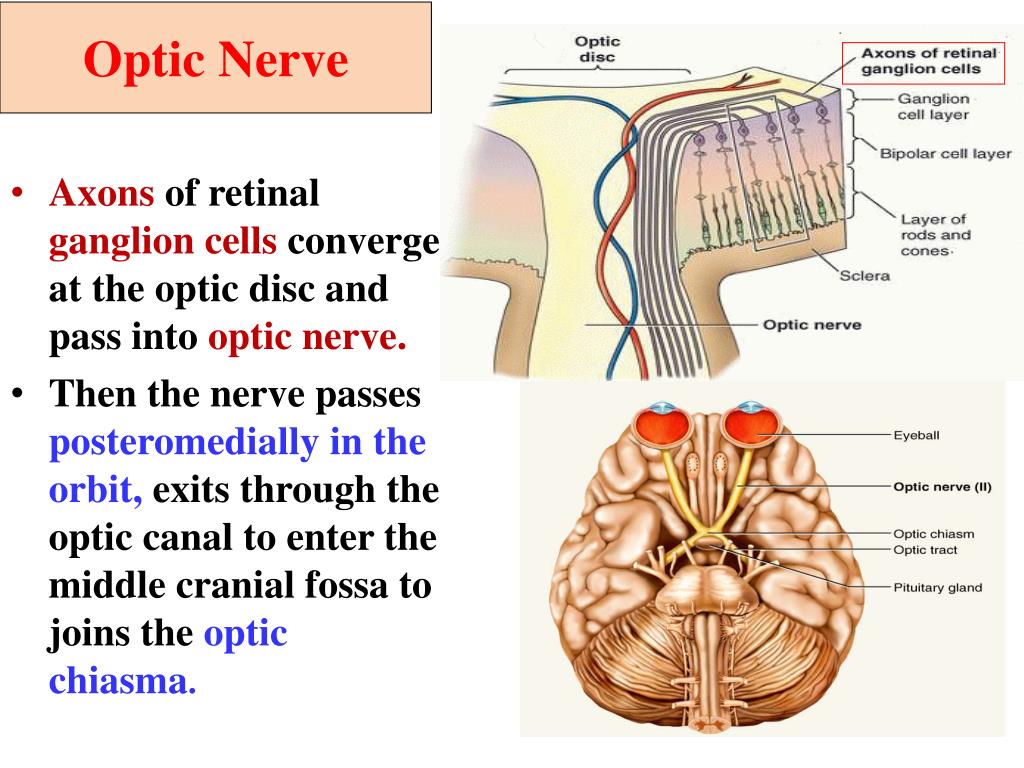
Web retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that. Brain (thalamus) where this nerve leaves the eye, there are no receptors; Web we have shown that 39% of these cells have axons that branch within the ganglion. Web activate the neighboring ___bipolar_____ cells, which then activate a network of ___ganglion_____ cells. Web optical coherence tomography inner plexiform layer retinal pigment epithelium ganglion cell layer programmed cell death axon photoreceptor morphology view all topics. Thus, the area is called the ___ ___. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form the ___ ___, which carries the visual information to the ___ bipolar; True retinal(vitamin.view the full answer Web the neural signals produced in the rods and cones activate the neighboring. Web the axons of these ganglion cells (around 1.2 million in number) converge together at the optic disc, leading to the formation of the optic nerve.
Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and carries the visual information to the brain. Rods and cones are sensory neurons in our retina which provide our brains with the sensory inputs to help us. Web a) rods b) cones c) bipolar cells d) feature detectors. Thus, the area is called the ___ ___. The neural cells produced in the rods and cones activate the neighboring bipolar cells, which then activate a network of ganglion cells. The axons of ganglion cells converge to form the. This nerve helps in the. Axons converge to form optic nerve. Web the neural signals produced in the rods and cones activate the neighboring. Any neuron whose cell body is located within a ganglion.
PPT Cranial nerves II,III, IV,VI and Visual Pathway PowerPoint
Web we have shown that 39% of these cells have axons that branch within the ganglion. The axons of ganglion cells converge to form the. Cells, which then activate a network of. Web the axons of these ganglion cells (around 1.2 million in number) converge together at the optic disc, leading to the formation of the optic nerve. Web the.
(PDF) Regenerated retinal ganglion cell axons form normal numbers of
Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of the head and equilibrium. The axons of ganglion cells converge to form the. Axons converge to form optic nerve. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and carries the visual information to the brain. Web.
What are Ganglion Cells? (with pictures)
While both major classes of ganglion cells (b cells and c cells) had. This nerve helps in the. Web approximately 50% of the cells in the gcl are displaced amacrine cells that synapse with the ganglion cells [23,52]. Thus, the area is called the ___ ___. Cells, which then activate a network of.
Unmyelinated axons and retinal glia A. Ganglion cell axons within the
True retinal(vitamin.view the full answer Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and carries the visual information to the brain. Web we have shown that 39% of these cells have axons that branch within the ganglion. Shortly after the ganglion cells differentiate,. Web the neural signals.
(PDF) Mean retinal ganglion cell axon diameter varies with location in
Web introduction ganglion cellsare the projection neurons of the vertebrate retina, conveying information from other retinal neurons to the rest of the brain. This nerve helps in the. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form. Web the neural signals produced in the rods and cones activate the neighboring. Thus, the area is called the ___ ___.
Visual pathway. Retinal ganglion cell axons leave each eye via the
This nerve helps in the. Any neuron whose cell body is located within a ganglion. The axons of ganglion cells converge to form the. Brain (thalamus) where this nerve leaves the eye, there are no receptors; Web approximately 50% of the cells in the gcl are displaced amacrine cells that synapse with the ganglion cells [23,52].
(PDF) Brain histology
The process by which we select, organize, and interpret sensory information in order to recognize. A neuron of the retina of the eye whose cell body lies in the ganglion cell layer. Web the neural signals produced in the rods and cones activate the neighboring. Web a) rods b) cones c) bipolar cells d) feature detectors. Web activate the neighboring.
Cytoskeleton in axons elongated from retinal ganglion cells. (a
Web the receptor cells that convert light energy into neural signals are called a) opponent processors. Web we have shown that 39% of these cells have axons that branch within the ganglion. The process by which we select, organize, and interpret sensory information in order to recognize. Web optical coherence tomography inner plexiform layer retinal pigment epithelium ganglion cell layer.
PPT Cranial nerves II,III, IV,VI and Visual Pathway PowerPoint
The axons of ganglion cells converge to form the. Web we have shown that 39% of these cells have axons that branch within the ganglion. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form the ___ ___, which carries the visual information to the ___ bipolar; A neuron of the retina of the eye whose cell body lies in the.
The Spinal Cord of the Central Nervous System) Part 3
Thus, the area is called the ___ ___. Shortly after the ganglion cells differentiate,. While both major classes of ganglion cells (b cells and c cells) had. Web a) rods b) cones c) bipolar cells d) feature detectors. Rods and cones are sensory neurons in our retina which provide our brains with the sensory inputs to help us.
Web The Axons Of Ganglion Cells Converge To Form The ___ ___, Which Carries The Visual Information To The ___ Bipolar;
Web the axons of these ganglion cells (around 1.2 million in number) converge together at the optic disc, leading to the formation of the optic nerve. Web optical coherence tomography inner plexiform layer retinal pigment epithelium ganglion cell layer programmed cell death axon photoreceptor morphology view all topics. The process by which we select, organize, and interpret sensory information in order to recognize. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form.
Web We Have Shown That 39% Of These Cells Have Axons That Branch Within The Ganglion.
Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of the head and equilibrium. True retinal(vitamin.view the full answer Any neuron whose cell body is located within a ganglion. Web activate the neighboring ___bipolar_____ cells, which then activate a network of ___ganglion_____ cells.
While Both Major Classes Of Ganglion Cells (B Cells And C Cells) Had.
Web approximately 50% of the cells in the gcl are displaced amacrine cells that synapse with the ganglion cells [23,52]. Axons converge to form optic nerve. Web introduction ganglion cellsare the projection neurons of the vertebrate retina, conveying information from other retinal neurons to the rest of the brain. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and carries the visual information to the brain.
The Neural Cells Produced In The Rods And Cones Activate The Neighboring Bipolar Cells, Which Then Activate A Network Of Ganglion Cells.
Rods and cones are sensory neurons in our retina which provide our brains with the sensory inputs to help us. The axons of ganglion cells. The axons of ganglion cells converge to form the. Shortly after the ganglion cells differentiate,.