Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Animals
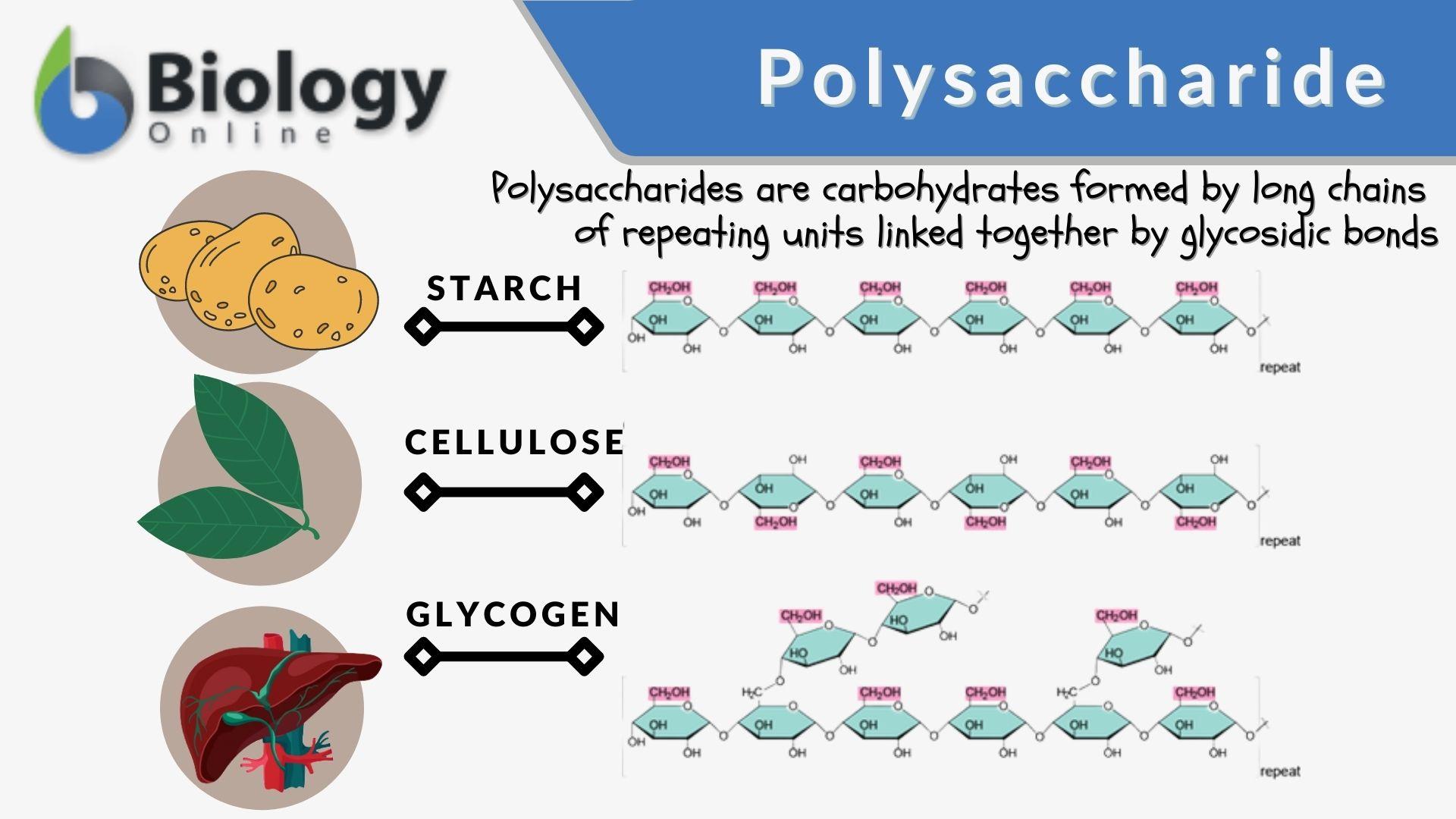
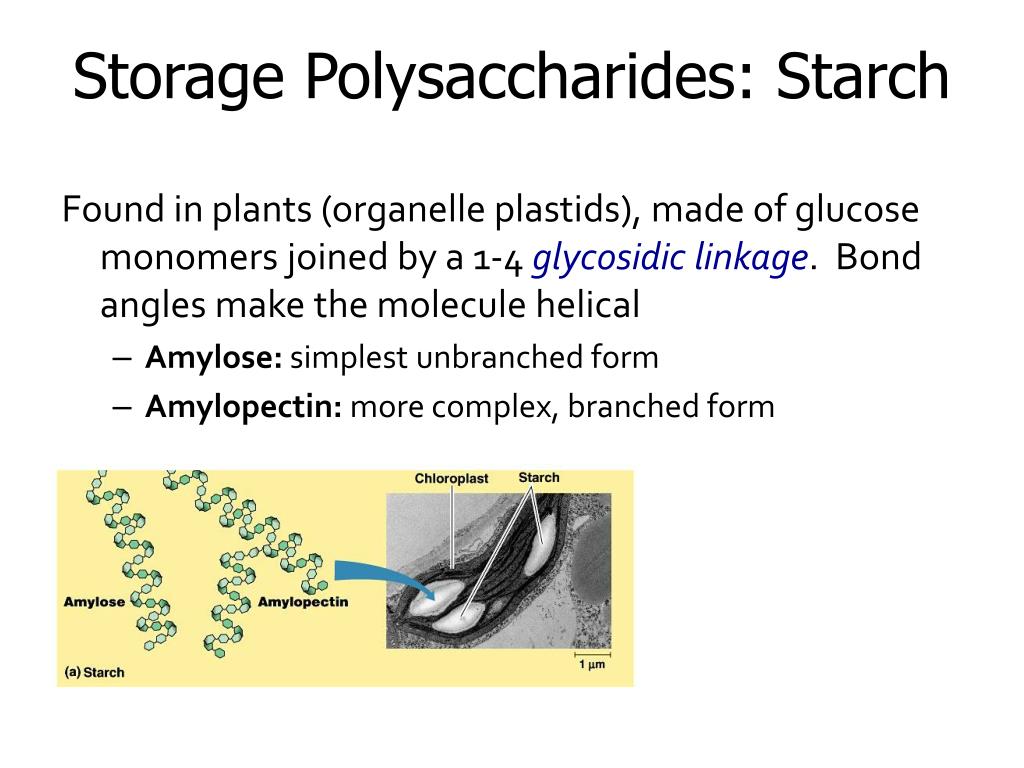
Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Animals - Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is comprised of monomers of glucose. Web animals do not store energy as starch. Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. These large polysaccharides contain many chemical bonds and therefore store a lot of chemical energy. Web animals store glucose primary in liver and muscle in the form of a compound related to amylopectin known as glycogen. When you eat french fries, potato chips, or a baked potato with all the fixings, enzymes in your digestive tract get to work on the long glucose chains, breaking them down into smaller sugars that your cells can use. Most monosaccharides in animal tissues are of 5 c and 6 c sugars. In both plants and animals, carbohydrates are the most efficient source of energy.
Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is comprised of monomers of glucose. Instead, animals store the extra energy as the complex carbohydrate glycogen. Most monosaccharides in animal tissues are of 5 c and 6 c sugars. When you eat french fries, potato chips, or a baked potato with all the fixings, enzymes in your digestive tract get to work on the long glucose chains, breaking them down into smaller sugars that your cells can use. Web monosaccharides are the simplest forms of carbohydrate. The structural differences between glycogen and amylopectin are solely due to the frequency of the alpha 1,6 branches of glucoses. Web animals store glucose primary in liver and muscle in the form of a compound related to amylopectin known as glycogen. Web the energy storage form of carbohydrates is \rule {2cm} {0.4pt} in animals and \rule {2cm} {0.4pt} in plants. Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose. Web animals do not store energy as starch.
It serves as a form of energy storage in fungi as well as animals and is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. Most monosaccharides in animal tissues are of 5 c and 6 c sugars. Web plants store carbohydrates in long polysaccharides chains called starch, while animals store carbohydrates as the molecule glycogen. The structural differences between glycogen and amylopectin are solely due to the frequency of the alpha 1,6 branches of glucoses. Web the energy storage form of carbohydrates is \rule {2cm} {0.4pt} in animals and \rule {2cm} {0.4pt} in plants. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose. Web animals do not store energy as starch. When you eat french fries, potato chips, or a baked potato with all the fixings, enzymes in your digestive tract get to work on the long glucose chains, breaking them down into smaller sugars that your cells can use.
Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Plants Plants BA
In both plants and animals, carbohydrates are the most efficient source of energy. A) starch, glycogen b) glycogen, cellulose c) glycogen, starch d) chitin, glycogen e). Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. These large polysaccharides contain many chemical bonds and therefore store a lot of.
Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Plants Plants BA
Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. The polymeric carbohydrate starch, also known as amylum, is made up of multiple glucose units joined by glycosidic. Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose. Most monosaccharides in animal tissues are of 5 c and 6 c sugars. These large.
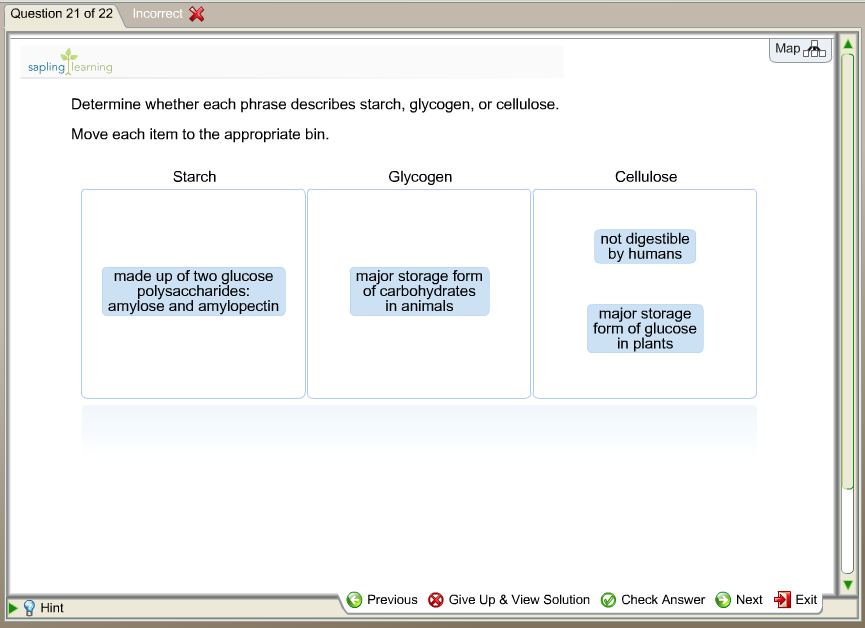
Solved Question 21 Of 22 Incorrect Map Sapling Learning D...
Most monosaccharides in animal tissues are of 5 c and 6 c sugars. Web the energy storage form of carbohydrates is \rule {2cm} {0.4pt} in animals and \rule {2cm} {0.4pt} in plants. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. The polymeric carbohydrate starch, also known as amylum,.
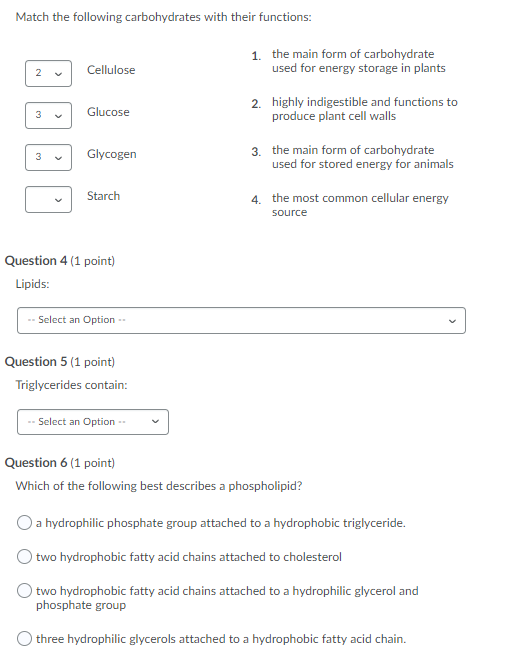
Solved Match the following carbohydrates with their
Web plants store carbohydrates in long polysaccharides chains called starch, while animals store carbohydrates as the molecule glycogen. Most monosaccharides in animal tissues are of 5 c and 6 c sugars. The structural differences between glycogen and amylopectin are solely due to the frequency of the alpha 1,6 branches of glucoses. Web part a the storage form of carbohydrates in.
Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Plants Plants BA
In both plants and animals, carbohydrates are the most efficient source of energy. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. A) starch, glycogen b) glycogen, cellulose c) glycogen, starch d) chitin, glycogen e). It serves as a form of energy storage in fungi as well as animals.
Energy Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Animals Printable Form
The structural differences between glycogen and amylopectin are solely due to the frequency of the alpha 1,6 branches of glucoses. Web monosaccharides are the simplest forms of carbohydrate. Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is comprised of monomers of glucose. A) starch, glycogen b) glycogen, cellulose c) glycogen, starch d) chitin, glycogen.
Carbohydrates Are Stored In Fhe Kiver And Musc In The Form Of
Web animals do not store energy as starch. These large polysaccharides contain many chemical bonds and therefore store a lot of chemical energy. A) starch, glycogen b) glycogen, cellulose c) glycogen, starch d) chitin, glycogen e). Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is comprised of monomers of glucose. They are stored as.
Carbohydrates Are Stored In Fhe Kiver And Musc In The Form Of Storage
Web plants store carbohydrates in long polysaccharides chains called starch, while animals store carbohydrates as the molecule glycogen. These large polysaccharides contain many chemical bonds and therefore store a lot of chemical energy. A) starch, glycogen b) glycogen, cellulose c) glycogen, starch d) chitin, glycogen e). Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually.
Name the major storage form of carbohydrates in animals?
Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Whenever blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen is broken down to release glucose in a process known as. Web glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is comprised of monomers of glucose. Glycogen is.
Biological role of carbohydrates
A) starch, glycogen b) glycogen, cellulose c) glycogen, starch d) chitin, glycogen e). Web animals store glucose primary in liver and muscle in the form of a compound related to amylopectin known as glycogen. Web monosaccharides are the simplest forms of carbohydrate. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and.
The Polymeric Carbohydrate Starch, Also Known As Amylum, Is Made Up Of Multiple Glucose Units Joined By Glycosidic.
Web part a the storage form of carbohydrates in animals check all that apply. Web most of the carbohydrate, though, is in the form of starch, long chains of linked glucose molecules that are a storage form of fuel. A) starch, glycogen b) glycogen, cellulose c) glycogen, starch d) chitin, glycogen e). They are stored as starch and glycogen form in plants and animals.
Web Glycogen Is The Storage Form Of Glucose In Humans And Other Vertebrates And Is Comprised Of Monomers Of Glucose.
It serves as a form of energy storage in fungi as well as animals and is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. Web monosaccharides are the simplest forms of carbohydrate.
Web Glycogen Is The Storage Form Of Glucose In Humans And Other Vertebrates And Is Made Up Of Monomers Of Glucose.
Simple sugars are also subdivided into aldose, a sugar that contains an aldehyde structure, or ketose, a sugar that contains a ketone group. In both plants and animals, carbohydrates are the most efficient source of energy. These large polysaccharides contain many chemical bonds and therefore store a lot of chemical energy. Whenever blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen is broken down to release glucose in a process known as.
Web Animals Do Not Store Energy As Starch.
Instead, animals store the extra energy as the complex carbohydrate glycogen. Web plants store carbohydrates in long polysaccharides chains called starch, while animals store carbohydrates as the molecule glycogen. When you eat french fries, potato chips, or a baked potato with all the fixings, enzymes in your digestive tract get to work on the long glucose chains, breaking them down into smaller sugars that your cells can use. The structural differences between glycogen and amylopectin are solely due to the frequency of the alpha 1,6 branches of glucoses.



/wholegrain-food-still-life-shot-on-rustic-wooden-table-835833518-5bf54e2c4cedfd00264d07fb.jpg)

