Milady Chapter 6 General Anatomy And Physiology
Milady Chapter 6 General Anatomy And Physiology - Web milady chapter 6 general anatomy & physiology (1) no teams 1 team 2 teams 3 teams 4 teams 5 teams 6 teams 7 teams. Web 120chapter 6 general anatomy and physiologypart 2: Web 206 bones, softer tissues and organs are attached. Web russ reads chapter 6 general anatomy and physiology of the milady standard barber text book aloud. Muscles are connected to the bones by tendons. Web the dense, active protoplasm found in the center of the cell. The study of the human body structure that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized. Is the study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked. Web chapter 6 milady general anatomy and physiology. Produce movement within the body.
Web chapter 6 milady general anatomy and physiology. Web milady chapter 6 general anatomy & physiology (1) no teams 1 team 2 teams 3 teams 4 teams 5 teams 6 teams 7 teams. Web ch 6 all milady and pivot point e. Muscles that seperate the fingers. Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and. Muscles are connected to the bones by tendons. The basic unit of all living things, from bacteria to plants. Web in this class we go over chapter 6 in the milady standard barbering textbook.we are discussing the review questions. It has different key terms and. Russ reads milady standard cosmetology.
Web 120chapter 6 general anatomy and physiologypart 2: The basic unit of all living things, from bacteria to plants. The watery fluid that surrounds the nucleus of the cell and is. Produce movement within the body. Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and. Web milady theory chapter 6. Web the study of human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized; Web this is a summary of chapter 6 of the milady fundamentals of esthetics textbook. Web the muscle of the forearm that rotates the radius outward and the palm upward is the ___. The study of the human body structure that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized.
Milady Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology (Circulatory) Diagram
Muscle of the foot that. Is the study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked. The watery fluid that surrounds the nucleus of the cell and is. General anatomy and physiology learning objectives: Web russ reads chapter 6 general anatomy and physiology of the milady standard barber text book aloud.
General Anatomy and Physiology Milady Chapter 6 Review Questions
Web in this class we go over chapter 6 in the milady standard barbering textbook.we are discussing the review questions. Web chapter 6 milady general anatomy and physiology. Muscle of the foot that. Russ reads milady standard cosmetology. Web 206 bones, softer tissues and organs are attached.
Milady Standard Barber text book chapter 6 General Anatomy and
The study of the human body structure that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized. Web the dense, active protoplasm found in the center of the cell. Produce movement within the body. Web ch 6 all milady and pivot point e. Muscle of the foot that.
Milady Cosmetology chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology flashcards
Web in this class we go over chapter 6 in the milady standard barbering textbook.we are discussing the review questions. Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and. The cells of all living thing are made up of protoplasm term: The basic unit of all living things, from bacteria to plants. The watery fluid that surrounds the nucleus of.
General Anatomy and Physiology Milady Standard Barbering Book Chapter
The basic unit of all living things, from bacteria to plants. Muscle of the foot that. Web ch 6 all milady and pivot point e. Web chapter 6 milady general anatomy and physiology. Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and.
Chapter 7 Milady Workbook Answers FerhanLouden
Web in this class we go over chapter 6 in the milady standard barbering textbook.we are discussing the review questions. Web ch 6 all milady and pivot point e. The cells of all living thing are made up of protoplasm term: It has different key terms and. Web 206 bones, softer tissues and organs are attached.
Milady Chapter 6 General Anatomy & Physiology Diagram Quizlet
Web this is a summary of chapter 6 of the milady fundamentals of esthetics textbook. Muscle of the foot that. Web the dense, active protoplasm found in the center of the cell. Web russ reads chapter 6 general anatomy and physiology of the milady standard barber text book aloud. Muscles are connected to the bones by tendons.
21+ Milady Chapter 6 Anatomy Test Answers SukverRuqqiya
Web the study of human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized; Web 120chapter 6 general anatomy and physiologypart 2: Web ch 6 all milady and pivot point e. The watery fluid that surrounds the nucleus of the cell and is. The basic unit of all living things, from bacteria.
Chapter 6 General Anatomy And Physiology
Produce movement within the body. Web chapter 6 milady general anatomy and physiology. Web a protective covering on body surfaces, such as skin, mucous membranes, the tissues inside the mouth, the lining of the heart,. Muscles are connected to the bones by tendons. Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and.
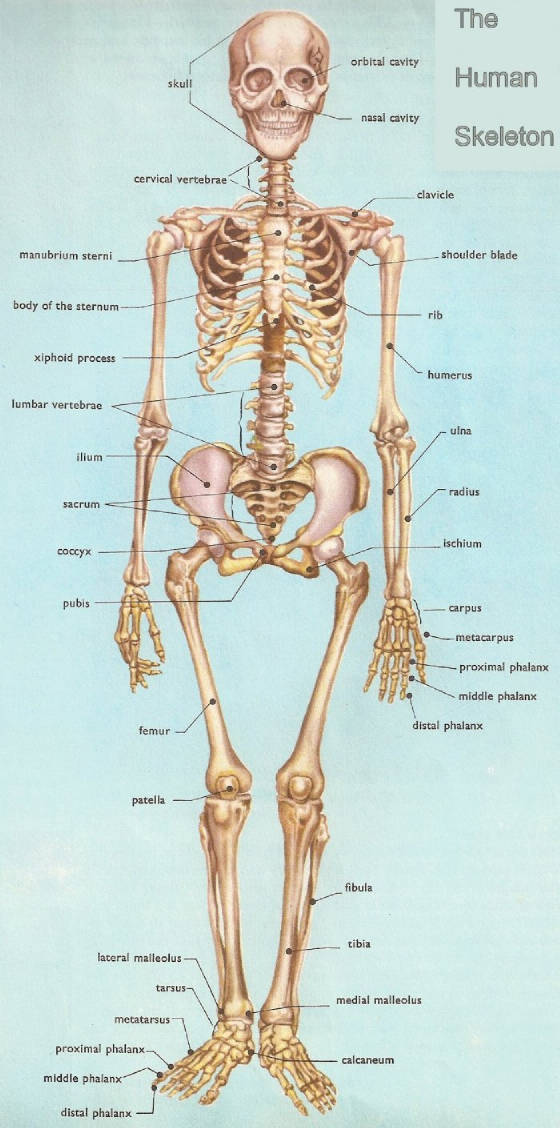
HumanSkeleton
Web the dense, active protoplasm found in the center of the cell. Muscles that seperate the fingers. Web milady chapter 6 general anatomy & physiology (1) no teams 1 team 2 teams 3 teams 4 teams 5 teams 6 teams 7 teams. The basic unit of all living things, from bacteria to plants. It has different key terms and.
Russ Reads Milady Standard Cosmetology.
General anatomy and physiology learning objectives: Muscles are connected to the bones by tendons. Web milady theory chapter 6. Muscles that seperate the fingers.
Web Milady Chapter 6 General Anatomy & Physiology (1) No Teams 1 Team 2 Teams 3 Teams 4 Teams 5 Teams 6 Teams 7 Teams.
Web chapter 6 milady general anatomy and physiology. Web the dense, active protoplasm found in the center of the cell. Muscle of the foot that. Web 206 bones, softer tissues and organs are attached.
Web Russ Reads Chapter 6 General Anatomy And Physiology Of The Milady Standard Barber Text Book Aloud.
The study of the human body structure that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized. Web the study of human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized; Produce movement within the body. The basic unit of all living things, from bacteria to plants.
Is The Study Of The Human Body Structures That Can Be Seen With The Naked.
Web the muscle of the forearm that rotates the radius outward and the palm upward is the ___. Web in this class we go over chapter 6 in the milady standard barbering textbook.we are discussing the review questions. Web 120chapter 6 general anatomy and physiologypart 2: Define and explain the importance of anatomy, physiology, and.