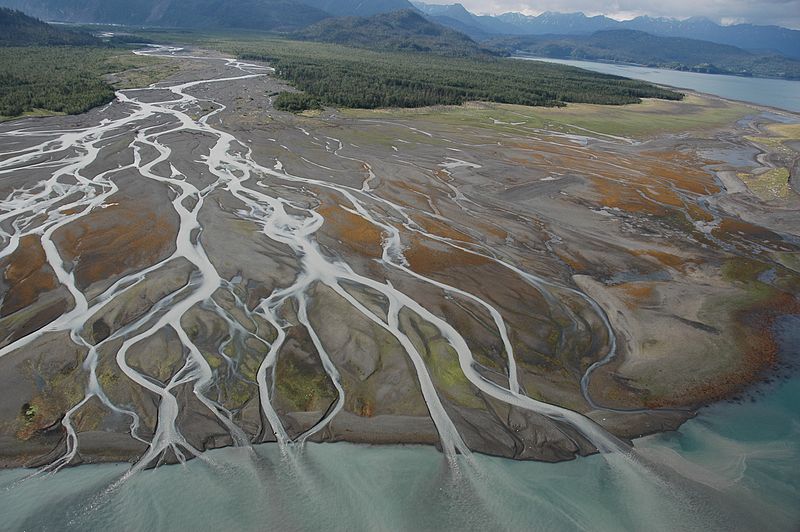
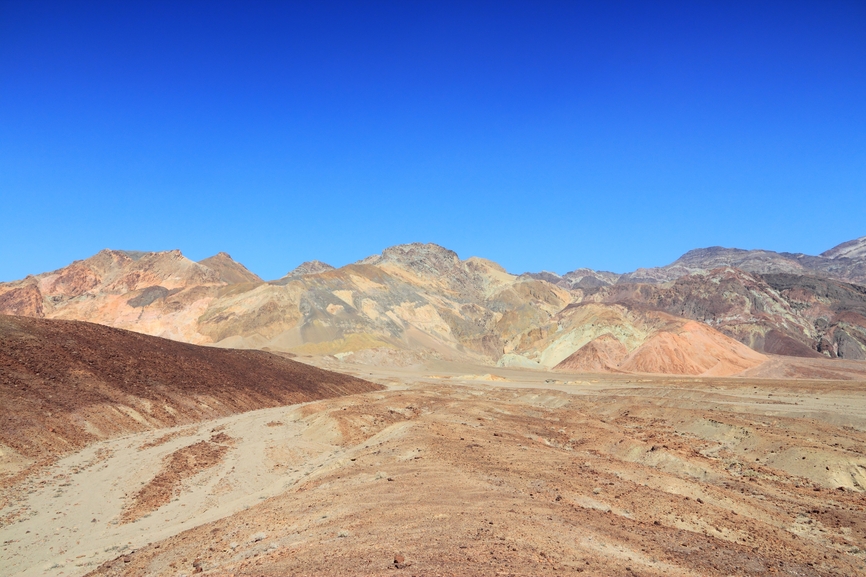
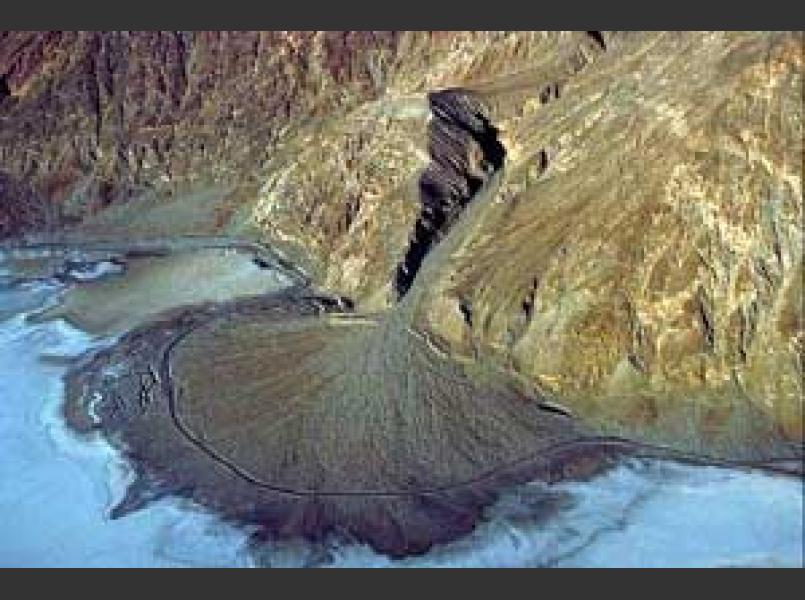
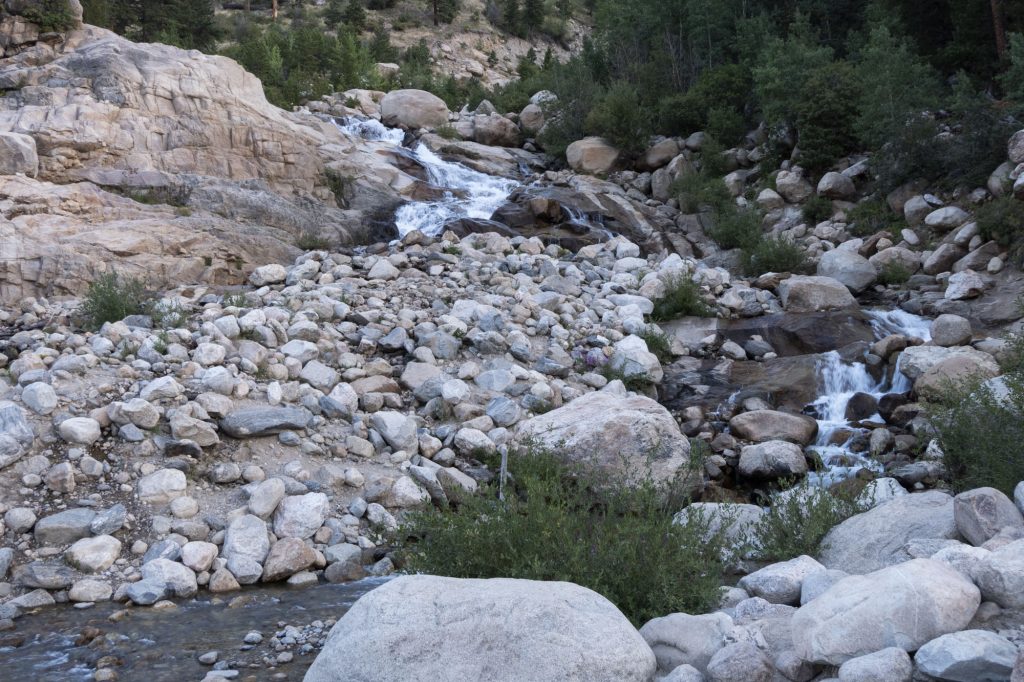
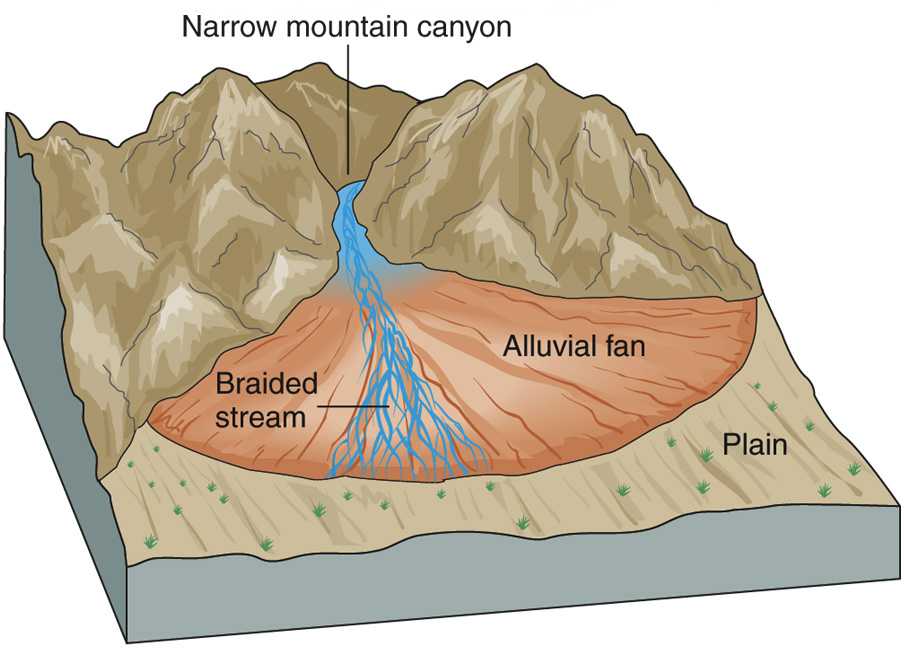
How Does An Alluvial Fan Form
How Does An Alluvial Fan Form - Web how does an alluvial fan form? Web alluvial fans form in areas with a steep gradient from a drainage catchment to the basin floor whereas wadis in valleys form where the gradients are much lower. When the sediment deposits into an ocean or lake, and a sloping deposit of sediment from a stream leaving a mountain. Web alluvial fans are a conspicuous conical landform commonly developed where a channel emerges from a mountainous catchment to an adjoining valley (figs. [1] tectonic movements such as tectonic uplift are driving factors in determining the. The apron of an alluvial fan can have length of just a few centimeters. Steep channels and other sediment sources feed out onto flat planes. Tectonic forces have been shown to have major influences on alluvial fans. Web how do alluvial fans form? Web alluvial fans form when flowing water passes through a narrow gap, such as between mountains, hills, or canyon walls.
How does an alluvial fan form? Web when does an alluvial fan form? The energy of the system drop dramatically, leading to the deposition of. Steep channels and other sediment sources feed out onto flat planes. The apron of an alluvial fan can have length of just a few centimeters. Tectonic activity is typically required to maintain steep slopes because. Web alluvial fans form in areas with a steep gradient from a drainage catchment to the basin floor. Web this video explains how alluvial fans are created and the contributing processes of erosion and weathering. Web alluvial fans form when flowing water passes through a narrow gap, such as between mountains, hills, or canyon walls. The flowing water picks up sediments and.
The apron of an alluvial fan can have length of just a few centimeters. Steep channels and other sediment sources feed out onto flat planes. When a stream with a steep gradient emerges onto a relatively flat lowland, its gradient drops, and it deposits. Web earth sciences questions and answers. [1] tectonic movements such as tectonic uplift are driving factors in determining the. Stream gradients decrease at the. We hope this video helps you learn more about. Web when does an alluvial fan form? Web alluvial fans form in areas with a steep gradient from a drainage catchment to the basin floor. Web an alluvial fan is defined as:
8 Main Types Of Streams
When a stream reached a flat area of land,slows down, and deposits sediment there over time what's the difference between erosion,weathering. Web alluvial fans form in areas with a steep gradient from a drainage catchment to the basin floor. When a stream with a steep gradient emerges onto a relatively flat lowland, its gradient drops, and it deposits. Web earth.
How Are Deltas And Alluvial Fans Formed Fan Review Information
The apex is the narrower part of the alluvial fan and the apron is the wide triangle. When a stream with a steep gradient emerges onto a relatively flat lowland, its gradient drops, and it deposits. Web how do alluvial fans form? Web when does an alluvial fan form? When a stream reached a flat area of land,slows down, and.
PPT HOW TO IDENTIFY AN ALLUVIAL FAN PowerPoint Presentation, free
The apex is the narrower part of the alluvial fan and the apron is the wide triangle. [1] tectonic movements such as tectonic uplift are driving factors in determining the. Tectonic activity is typically required to maintain steep slopes because. The apron of an alluvial fan can have length of just a few centimeters. Web earth sciences questions and answers.
Alluvial Fan
Web an alluvial fan is defined as: Web alluvial fans form when flowing water passes through a narrow gap, such as between mountains, hills, or canyon walls. Web parts of an alluvial fan. When a stream with a steep gradient emerges onto a relatively flat lowland, its gradient drops, and it deposits. How do alluvial fans form?
Alluvial AJU
The flowing water picks up sediments and. Web alluvial fans are a conspicuous conical landform commonly developed where a channel emerges from a mountainous catchment to an adjoining valley (figs. Web parts of an alluvial fan. How do alluvial fans form? Web how does an alluvial fan form?
Definitions Fish Friendly Farming
[1] tectonic movements such as tectonic uplift are driving factors in determining the. We hope this video helps you learn more about. How do alluvial fans form? The flowing water picks up sediments and. Web when does an alluvial fan form?
Alluvial Fan Flashcards, Fan, Understanding
[1] tectonic movements such as tectonic uplift are driving factors in determining the. We hope this video helps you learn more about. Web how does an alluvial fan form? The energy of the system drop dramatically, leading to the deposition of. Web this video explains how alluvial fans are created and the contributing processes of erosion and weathering.
Landforms in the World Fluvial Landform ( 02.Alluvial Fan )
Web an alluvial fan is defined as: The apex is the narrower part of the alluvial fan and the apron is the wide triangle. The energy of the system drop dramatically, leading to the deposition of. Tectonic activity is typically required to maintain steep slopes because. How does an alluvial fan form?
Alluvial Fan Hike 734
Tectonic activity is typically required to maintain steep slopes because. We hope this video helps you learn more about. The energy of the system drop dramatically, leading to the deposition of. Tectonic forces have been shown to have major influences on alluvial fans. Web alluvial fans form in areas with a steep gradient from a drainage catchment to the basin.
What is the Difference Between Alluvial Fan and Delta
Steep channels and other sediment sources feed out onto flat planes. The apex is the narrower part of the alluvial fan and the apron is the wide triangle. Web alluvial fans form when flowing water passes through a narrow gap, such as between mountains, hills, or canyon walls. When the sediment deposits into an ocean or lake, and a sloping.
Web When Does An Alluvial Fan Form?
We hope this video helps you learn more about. Web how does an alluvial fan form? How does an alluvial fan form? Steep channels and other sediment sources feed out onto flat planes.
How Do Alluvial Fans Form?
Stream gradients decrease at the. When the sediment deposits into an ocean or lake, and a sloping deposit of sediment from a stream leaving a mountain. Web an alluvial fan is defined as: The apex is the narrower part of the alluvial fan and the apron is the wide triangle.
When A Stream With A Steep Gradient Emerges Onto A Relatively Flat Lowland, Its Gradient Drops, And It Deposits.
Web alluvial fans form in areas with a steep gradient from a drainage catchment to the basin floor. Web alluvial fans form in areas with a steep gradient from a drainage catchment to the basin floor whereas wadis in valleys form where the gradients are much lower. The energy of the system drop dramatically, leading to the deposition of. Web alluvial fans developed from the lower limit of lahar deposits produced by the volcanic mountain ranges covering the southern limit of the nicaragua graben.
Web This Video Explains How Alluvial Fans Are Created And The Contributing Processes Of Erosion And Weathering.
Web alluvial fans are a conspicuous conical landform commonly developed where a channel emerges from a mountainous catchment to an adjoining valley (figs. Tectonic activity is typically required to maintain steep slopes because. The flowing water picks up sediments and. Tectonic forces have been shown to have major influences on alluvial fans.