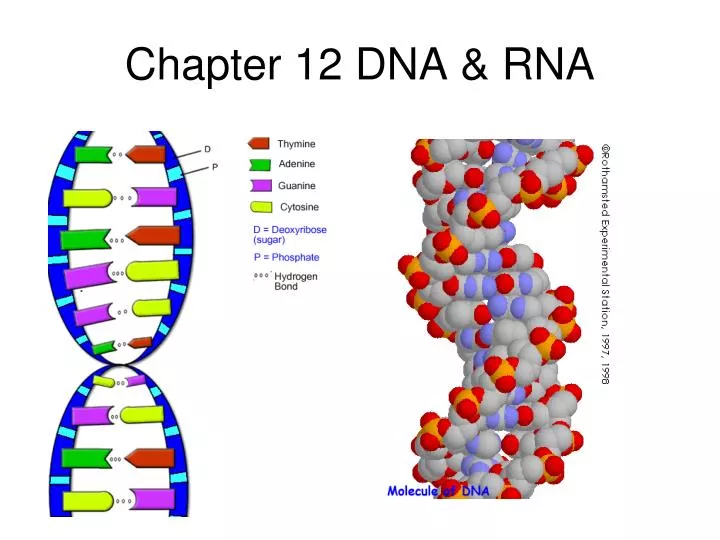
Dna And Rna Chapter 12
Dna And Rna Chapter 12 - In corn plants, having kernel color (c) is recessive to the gene that inhibits kernel color (c). Web summarize the synthesis of mrna. D) genetic material is found in protein: Web type of rna molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis transcription process in which part of the nucleotide sequence of dna is copied into a complementary sequence in rna The principal enzyme involved in dna replication. Genes coded dna instructions that control the production of proteins within. Molecular genetics chapter test practice. Web key for chapter 12 dna and rna. Web dna bases can be damaged by: C) dna and rna are in living things:
Dna and rna control protein synthesis: Web summarize the synthesis of mrna. Granular material visible within the nucleus. Which substance shown here, binds to the site where messenger rna. Web dna bases can be damaged by: C) dna and rna are in living things: The principal enzyme involved in dna replication is _ because it joins indiviual nucleotides to produce a dna molecule. Genes coded dna instructions that control the production of proteins within. The principal enzyme involved in dna replication. (1) oxidative processes, (2) alkylation of bases, (3) base loss caused by the hydrolysis of bases, (4) bulky adduct formation, (5) dna crosslinking, and (6) dna strand breaks, including.
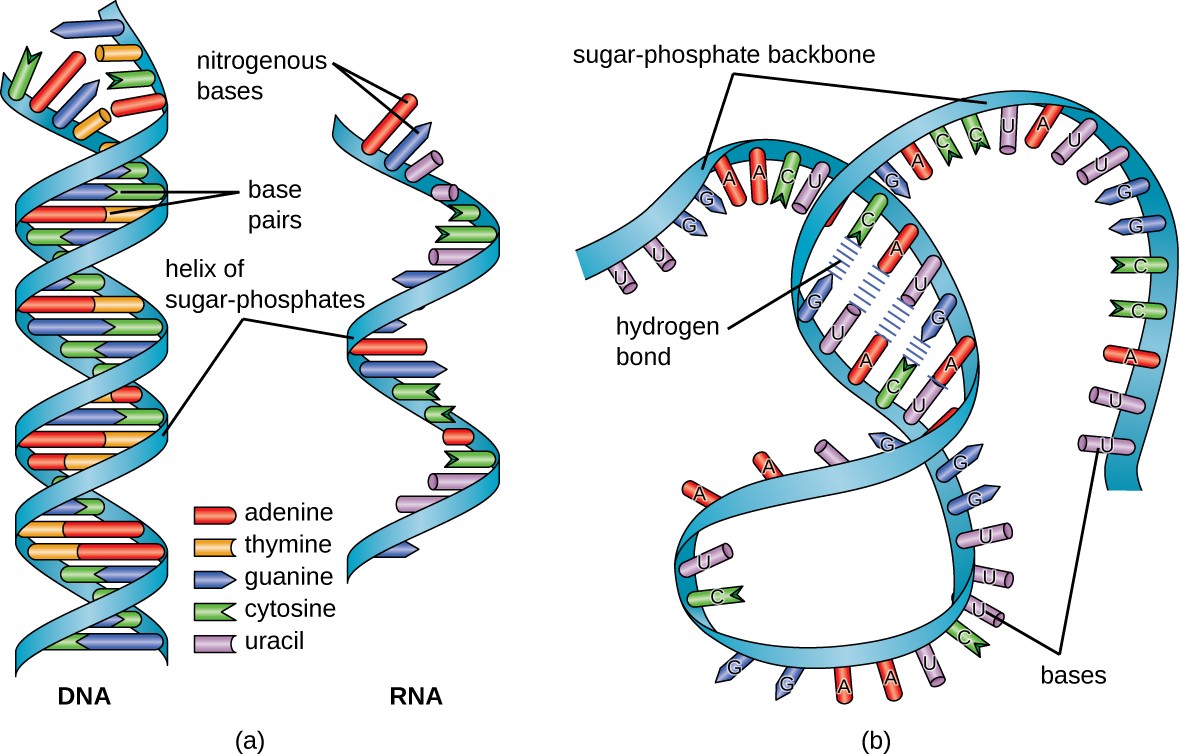
Web summarize the synthesis of mrna. Process in which dna makes a copy of itself. Web terms in this set (45) transcription. The mrna transcript is manufactured in the 5 to 3 direction, and. The principal enzyme involved in dna replication. Dna and rna control protein synthesis: Web the dna molecule separates into two strands, then produces two new complementary strands following the rules of base pairing. Web rna has ribose as sugar instead of deoxyribose, rna is single stranded while dna is double stranded, rna contains uracil in the place of thymine what are the three structural differences between dna and. Color appears when the homozygous condition is present. Granular material visible within the nucleus.
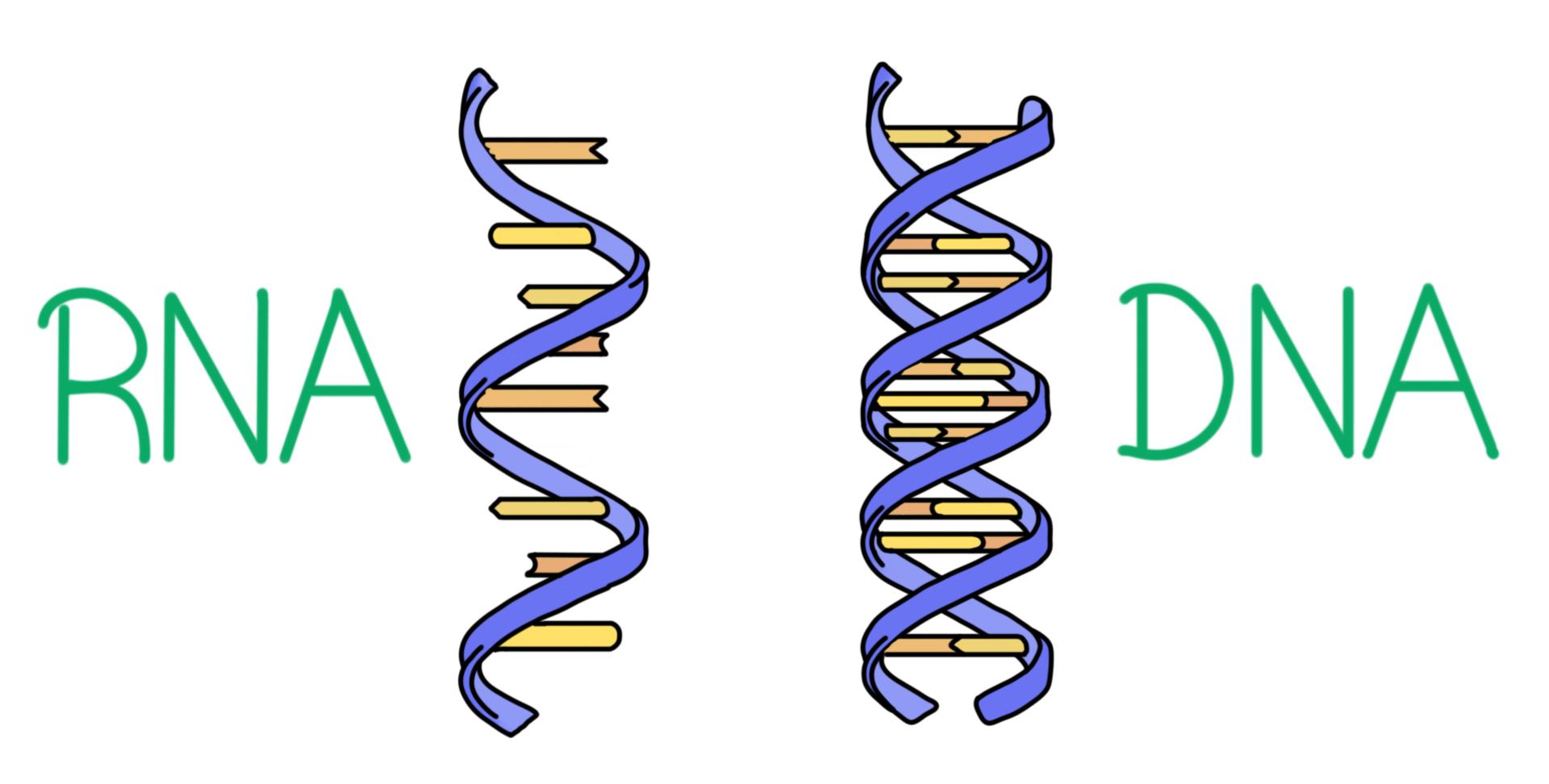
DNA vs RNA Similarities and Differences
Process in which dna makes a copy of itself. Each strand of the double helix of dna serves as a template for the new strand. Web the dna molecule separates into two strands, then produces two new complementary strands following the rules of base pairing. Web dna bases can be damaged by: It also describes the chemical structure of the.
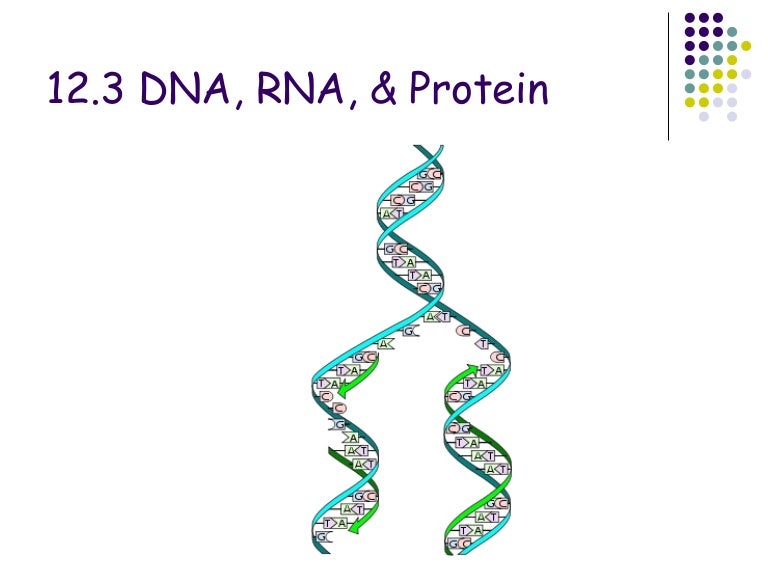
Chapter 12.3 dna,rna and protein
It explains its history, its structure and its function. It also describes the chemical structure of. In corn plants, having kernel color (c) is recessive to the gene that inhibits kernel color (c). Which substance shown here, binds to the site where messenger rna. The principal enzyme involved in dna replication.
Structure and Function of RNA Microbiology
Color appears when the homozygous condition is present. The principal enzyme involved in dna replication is _ because it joins indiviual nucleotides to produce a dna molecule. Process in which dna makes a copy of itself. The mrna transcript is manufactured in the 5 to 3 direction, and. C) dna and rna are in living things:
DNA vs. RNA — Differences & Similarities Expii
Is the process by which enzymes make an rna copy of a dna strand. They are nucleic acids, both have four bases, adenine, cytosine, guanine. It explains its history, its structure and its function. Web key for chapter 12 dna and rna. Color appears when the homozygous condition is present.
PPT Chapter 12 DNA & RNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web dna bases can be damaged by: Web terms in this set (45) transcription. Molecular genetics chapter test practice. The dna is unzipped, and rna polymerase binds to the template strand of the dna and moves in the 3 to 5 direction. The principal enzyme involved in dna replication is _ because it joins indiviual nucleotides to produce a dna.
The Differences Between DNA and RNA Explained With Diagrams Owlcation
C) dna and rna are in living things: Molecular genetics chapter test practice. Region of dna that indicates to an enzyme where to bind to make rna. Web dna bases can be damaged by: Which substance shown here, binds to the site where messenger rna.
Chapter 12 DNA & RNA Test
Dna and rna flashcards learn test match dna click the card to flip 👆 a long molecule made up of nucleotides that stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of an organism to the. Web biology chapter 12 and 13 dna and rna 5.0 (2 reviews) flashcards learn test match frederick griffith click the card to flip 👆.
RNA vs DNA the Differences DNA Encyclopedia
What are the similarties between dna and rna? Web eukaryotic chromosomes contain both dna and protein, tightly packed together to form a substance called _. The mrna transcript is manufactured in the 5 to 3 direction, and. The principal enzyme involved in dna replication is _ because it joins indiviual nucleotides to produce a dna molecule. (1) oxidative processes, (2).
DNA vs RNA Introduction and Differences between DNA and RNA
Is the process by which enzymes make an rna copy of a dna strand. Web eukaryotic chromosomes contain both dna and protein, tightly packed together to form a substance called _. This chapter also explains the roles of the different types of rna… Rna single stranded, 3 kinds of rna, has uracil and located in cytoplasm and nucleus; The mrna.
RNA Transcription Page 2 Chloe's Science
(1) oxidative processes, (2) alkylation of bases, (3) base loss caused by the hydrolysis of bases, (4) bulky adduct formation, (5) dna crosslinking, and (6) dna strand breaks, including. What are the similarties between dna and rna? Granular material visible within the nucleus. Region of dna that indicates to an enzyme where to bind to make rna. D) genetic material.
Web Key For Chapter 12 Dna And Rna.
(1) oxidative processes, (2) alkylation of bases, (3) base loss caused by the hydrolysis of bases, (4) bulky adduct formation, (5) dna crosslinking, and (6) dna strand breaks, including. Molecular genetics chapter test practice. Web eukaryotic chromosomes contain both dna and protein, tightly packed together to form a substance called _. A single stranded molecule of trna is produced.
They Are Nucleic Acids, Both Have Four Bases, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine.
Granular material visible within the nucleus. Web terms in this set (45) transcription. What are the similarties between dna and rna? Dna and rna control protein synthesis:
The Principal Enzyme Involved In Dna Replication Is _ Because It Joins Indiviual Nucleotides To Produce A Dna Molecule.
Color appears when the homozygous condition is present. The principal enzyme involved in dna replication. C) dna and rna are in living things: Web dna bases can be damaged by:
Duplication Of Dna Is Called _.
Which substance shown here, binds to the site where messenger rna. Grade 12 dna, rna, and genetics. Each strand of the double helix of dna serves as a template for the new strand. Rna single stranded, 3 kinds of rna, has uracil and located in cytoplasm and nucleus;

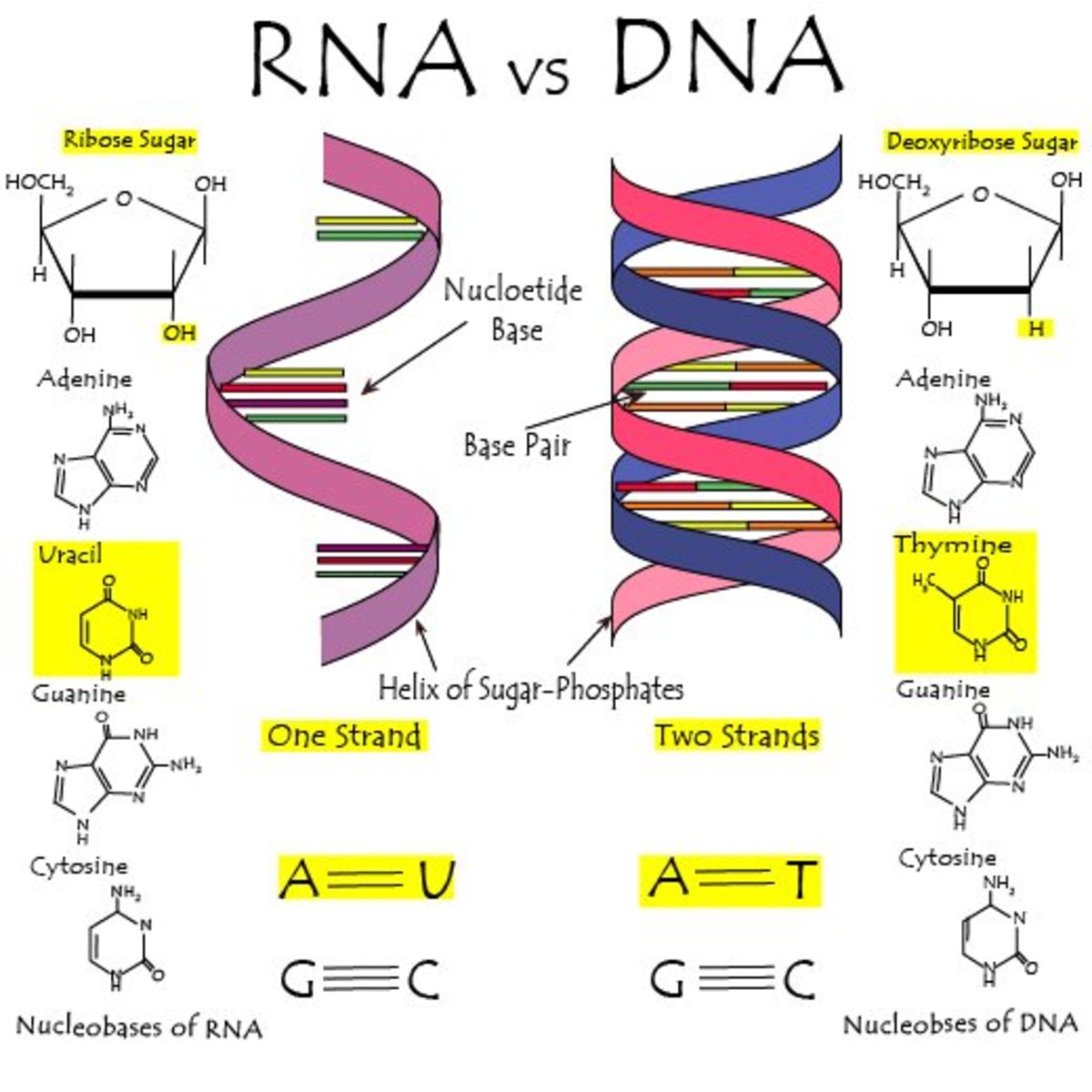


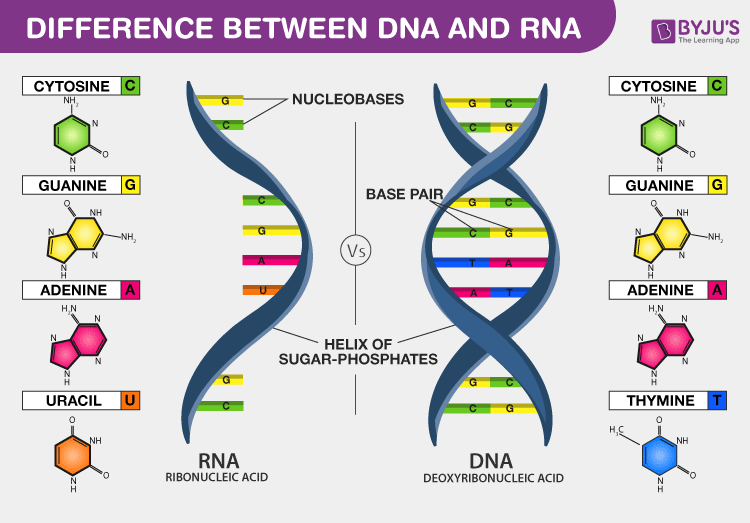
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)