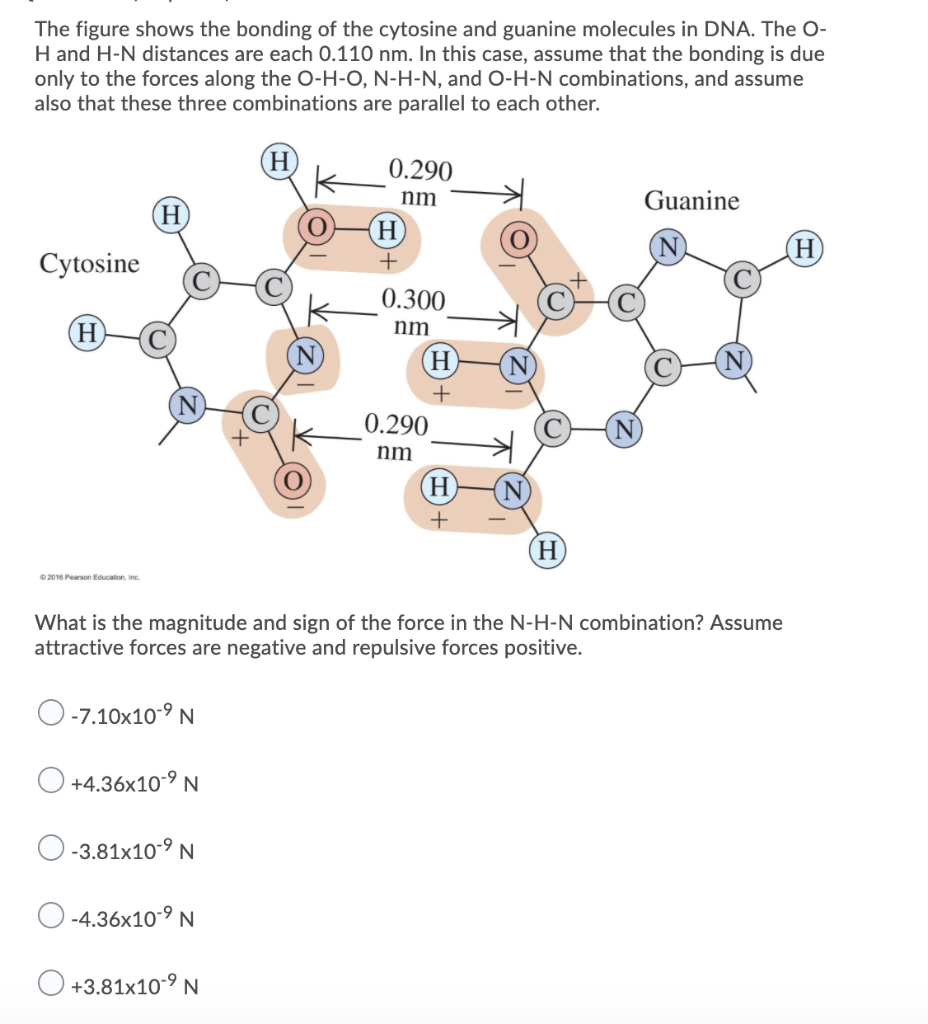
Cytosine And Guanine Form Three Hydrogen Bonds Between One Another
Cytosine And Guanine Form Three Hydrogen Bonds Between One Another - Or, more simply, c bonds with g. True false this problem has been solved! Web guanine pairs with cytosine with 3 hydrogen bonds [6].this creates a difference in strength between the two sets of watson and crick bases. Web you see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine can form two hydrogen bonds with thymine. 1 mixtures can form a planar dimer stabilized by three hydrogen bonds. True false true/false this problem has been solved! Web the number of hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine; Web the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. And between adenine and thymine in dna are:
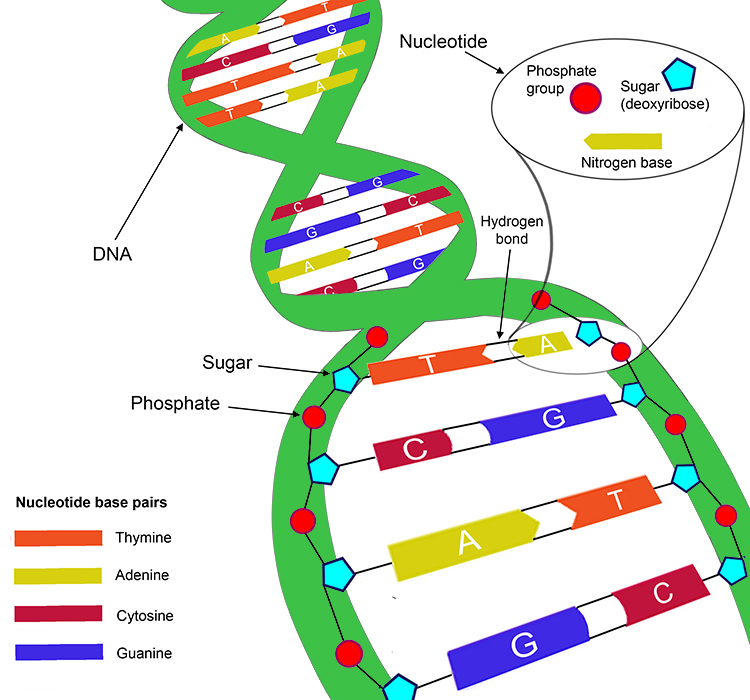
Two base pairs are produced by four nucleotide monomers, nucleobases are in blue. How many hydrogen bonds can be formed between molecules of. Qualitatively, guanine (g) and cytosine (c) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (a) bonds specifically with thymine (t) in dna and. Web properties guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both dna and rna, whereas thymine is usually seen only in dna, and uracil only in rna. Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another are the true statement. A nitrogenous base is part of the structure of the dna molecule. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. Web in dna, adenine (a) and thymine (t) are complementary base pairs, and cytosine (c) and guanine (g) are also complementary base pairs, explaining chargaff’s rules. True false true/false this problem has been solved! Guanine (g) is one of the four nucleotide bases in dna, with the other three being adenine (a), cytosine (c) and thymine (t).
Web you see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine can form two hydrogen bonds with thymine. Qualitatively, guanine (g) and cytosine (c) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (a) bonds specifically with thymine (t) in dna and. A nitrogenous base is part of the structure of the dna molecule. Web biology biology questions and answers cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. Web the base pairing in dna between molecules of guanine and cytosine is shown in the given structure. Or, more simply, c bonds with g. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject. True false true/false this problem has been solved! Guanine (g) is one of the four nucleotide bases in dna, with the other three being adenine (a), cytosine (c) and thymine (t). Web hydrogen bond between guanine and cytosine | guanine cytosine base pair | nitrogenous base pairing nitrogenous base pairing in dna, in dna double helix structure.
Solved Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds
Web guanine bonds to cytosine because they both share three hydrogen bonds. A nitrogenous base is part of the structure of the dna molecule. Web properties guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both dna and rna, whereas thymine is usually seen only in dna, and uracil only in rna. True false this problem has been solved! When.
Hydrogen bonds in nucleotides cytosine and guanine
Two base pairs are produced by four nucleotide monomers, nucleobases are in blue. Web that monomeric guanine and cytosine in 1 : Web you see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine can form two hydrogen bonds with thymine. Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another are the true statement. When a nucleotide.
4 Base pairs in DNA. Panel (a) shows the guaninecytosine (GC) hydrogen
When a nucleotide in one chain of dna or rna has guanine as its base, the. Web the base pairing in dna between molecules of guanine and cytosine is shown in the given structure. Density functional theory is used to study the hydrogen bonding pattern in cytosine, which does not contain alternating proton donor and acceptor sites. A nitrogenous base.
Solved Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds
Web you see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine can form two hydrogen bonds with thymine. True false true/false this problem has been solved! Guanine (g) is one of the four nucleotide bases in dna, with the other three being adenine (a), cytosine (c) and thymine (t). Web the number of hydrogen bonds between guanine and.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
And between adenine and thymine in dna are: 1 mixtures can form a planar dimer stabilized by three hydrogen bonds. Web the number of hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine; Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. L), formed by monomers in nonaqueous.
Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule
Web hydrogen bond between guanine and cytosine | guanine cytosine base pair | nitrogenous base pairing nitrogenous base pairing in dna, in dna double helix structure. Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. A nitrogenous base is part of the structure of the dna molecule. Two base pairs are produced by four nucleotide monomers, nucleobases are.
DNA. Structure and Replication Presentation Biology
Web hydrogen bond between guanine and cytosine | guanine cytosine base pair | nitrogenous base pairing nitrogenous base pairing in dna, in dna double helix structure. Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. A nitrogenous base is part of the structure of the dna molecule. L), formed by monomers in nonaqueous. Web properties guanine, along with.
Solved The figure shows the bonding of the cytosine and
Two base pairs are produced by four nucleotide monomers, nucleobases are in blue. Web properties guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both dna and rna, whereas thymine is usually seen only in dna, and uracil only in rna. Web in dna, adenine (a) and thymine (t) are complementary base pairs, and cytosine (c) and guanine (g) are.
Solved Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds
When a nucleotide in one chain of dna or rna has guanine as its base, the. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. How many hydrogen bonds can be formed between molecules of. Web biology biology questions and answers cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between.
The number of hydrogen bonds between cytosine (C) and guanine (G) is
L), formed by monomers in nonaqueous. And between adenine and thymine in dna are: True false true/false this problem has been solved! Web that monomeric guanine and cytosine in 1 : Web guanine bonds to cytosine because they both share three hydrogen bonds.
Web Properties Guanine, Along With Adenine And Cytosine, Is Present In Both Dna And Rna, Whereas Thymine Is Usually Seen Only In Dna, And Uracil Only In Rna.
Web the base pairing in dna between molecules of guanine and cytosine is shown in the given structure. 1 mixtures can form a planar dimer stabilized by three hydrogen bonds. Web the number of hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine; Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another.
Web That Monomeric Guanine And Cytosine In 1 :
Web guanine bonds to cytosine because they both share three hydrogen bonds. Two base pairs are produced by four nucleotide monomers, nucleobases are in blue. Web guanine pairs with cytosine with 3 hydrogen bonds [6].this creates a difference in strength between the two sets of watson and crick bases. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another.
And Between Adenine And Thymine In Dna Are:
Web cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another are the true statement. Web biology biology questions and answers cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. Qualitatively, guanine (g) and cytosine (c) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (a) bonds specifically with thymine (t) in dna and. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
L), Formed By Monomers In Nonaqueous.
True false this problem has been solved! Web in dna, adenine (a) and thymine (t) are complementary base pairs, and cytosine (c) and guanine (g) are also complementary base pairs, explaining chargaff’s rules. Web you see, cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine can form two hydrogen bonds with thymine. Guanine (g) is paired with cytosine (c) via three hydrogen.



.PNG)