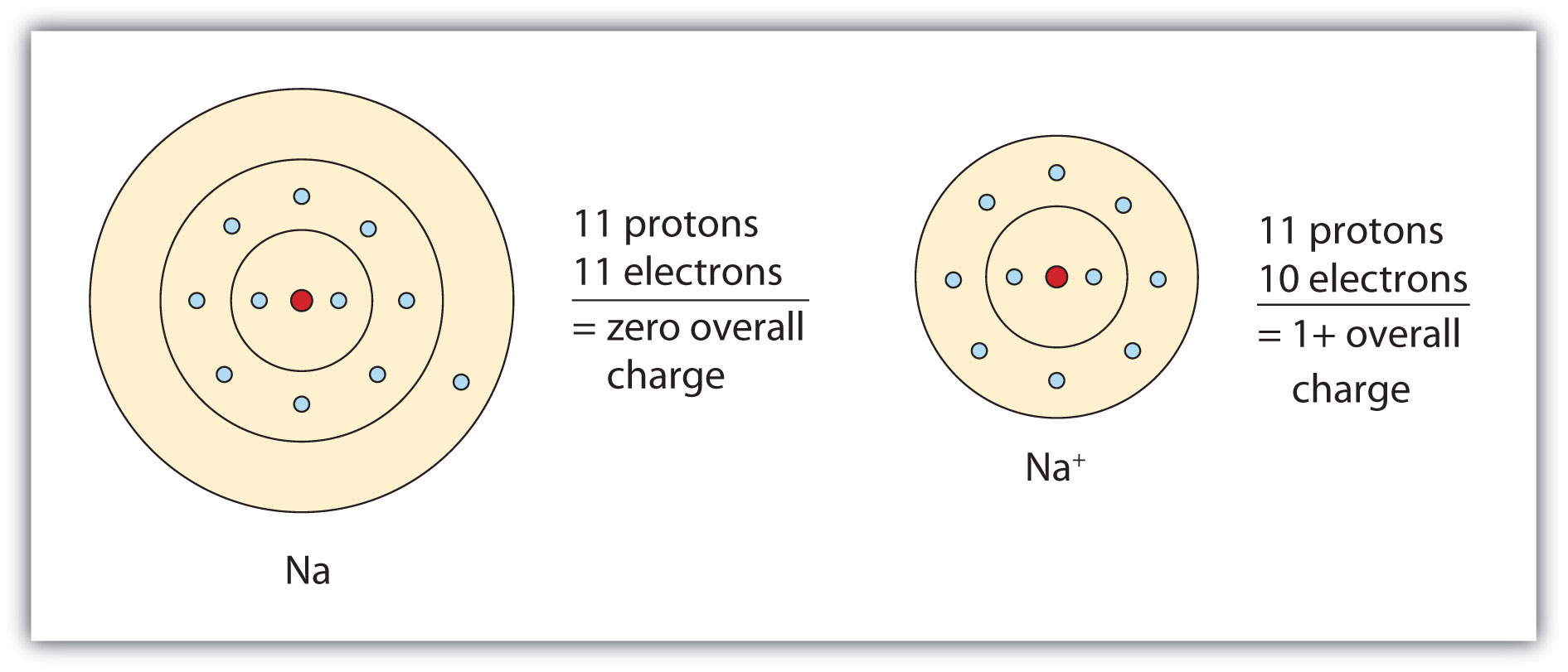
Chapter 6 Ions Charged Particles In Solution
Chapter 6 Ions Charged Particles In Solution - Web what path does the particle follow? Describe the differences among strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. The process of forming ions. Web when hydrogen becomes positively charged. Web chapter 6 ions charged particles in solution ionization process of forming ions hydrogen ion hydrogen atom becomes a positively charged hydrogen ion ht hydronium ion hydrogen atom bonded to a water molecule is called a hydronium ion h o hydroxide ion the oh group becomes a negatively charged hydroxide ion. Process of forming ions at any time a small number of molecules in a volume of water are separating into ions and them recombining Chemical substance with a positive charge, below 7.0 on the ph scale; Chemical substance with a negative charge; In an electrolyte, the electric current is carried by charged particles (ions) in solution. Web chapter 6 ions charged particles in solution worksheet answers 1 jonah:
Learn faster with spaced repetition. Positively charged hydrogen atom, symbolized as h+. Substances that produce hydrogen or hydronium ions. Web in solid form, an ionic compound is not electrically conductive because its ions are unable to flow (“electricity” is the flow of charged particles). > opposite charges of it may form ionic bonds. You will also be defining the terms, acids, bases, and salts. Chemical substance with a positive charge, below 7.0 on the ph scale; Web terms in this set (34) ion. An) complete the following statements about ions. Thus, solution containing ions are called electrolytes.
Web question:.68% chapter 6 lons: Hydrogen atom bonded to a water molecule, symbolized as h30+. Process of forming ions at any time a small number of molecules in a volume of water are separating into ions and them recombining > opposite charges of it may form ionic bonds. When molten, however, it can conduct electricity because its ions. Ostate how the ph scale is used to identify. The simplest case occurs when a charged. Web chapter 6 ions charged particles in solution worksheet answers 1 jonah: Web devionne_brown process of forming ions. J on the clock in chapter 6 ions:
PPT Review items for b asic chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free
The simplest case occurs when a charged. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study. > opposite charges of it may form ionic bonds. In an electrolyte, the electric current is carried by charged particles (ions) in solution. Pure water is not just a group of h 2 o molecules.
Principles of Food Science 5e, Lab Manual page 75
Then arrange the circled letters to fill in the statement about ions at the bottom of the page is a positively charged hydrogen atom 2. Substances that produce hydrogen or hydronium ions. (b) in a colloid, such as milk, the particles are much larger but remain dispersed and do not settle. The simplest case occurs when a charged. You feel.
Applied Chapter 5.1 Simple Ions
Describe how an aqueous solution is formed from both ionic compounds and molecular compounds. In this section, we discuss the circular motion of the charged particle as well as other motion that results from a charged particle entering a magnetic field. What is not a possible value for the charge on an ion in solution? In an electrolyte, the electric.
CH150 Chapter 3 Ions and Ionic Compounds Chemistry
When molten, however, it can conduct electricity because its ions. An) complete the following statements about ions. (b) in a colloid, such as milk, the particles are much larger but remain dispersed and do not settle. Chemical substance with a positive charge, below 7.0 on the ph scale; An ionic compound is made up of charged particles, called ions.
Pitt Medical Neuroscience Membrane Potentials
Charged particles in solution what's the charge? It has a giant lattice structure with strong electrostatic forces of attraction. Our body contains ions, too. Charged particles or particles that have an imbalance of electrons and protons. Pure water is not just a group of h 2 o molecules.
Solved The sum of all of the chemical reactions that occur
Then arrange the circled letters to fill in the statement about ions at the bottom of the page is a positively charged hydrogen atom 2. Describe how an aqueous solution is formed from both ionic compounds and molecular compounds. Charged particles or particles that have an imbalance of electrons and protons. The process of forming ions. Plants obtain positively charged.
Grade 9 CHAPTER5 IDENTIFYING IONS SEMESTER 2
Pure water is not just a group of h 2 o molecules. Web learning outcomes define a solution and describe the parts of a solution. Web when hydrogen becomes positively charged. An ionic compound is made up of charged particles, called ions. Web we will look at charged particles in solution.
Chapter 6 Ions YouTube
Our body contains ions, too. Charged particles in solutionon october 6 we will go to webb at 3:20 p.m. > charged particles tat have an imbalance of electrons and protons. Process of forming ions at any time a small number of molecules in a volume of water are separating into ions and them recombining Positively charged hydrogen atom, symbolized as.
Principles of Food Science, 4th Edition page xiii
J on the clock in chapter 6 ions: Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study. Chemical substance with a negative charge; You feel thirsty after playing. The process of forming ions.
Ions Charged Particles YouTube
Describe the differences among strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Defining acids and bases a. Odistinguish btw characteristics of acids and the characteristics of bases. Are factors in food preservation and wine,. When molten, however, it can conduct electricity because its ions.
Web We Will Look At Charged Particles In Solution.
> charged particles tat have an imbalance of electrons and protons. Web acids, bases and salts. Process of forming ions at any time a small number of molecules in a volume of water are separating into ions and them recombining > opposite charges of it may form ionic bonds.
Chemical Substance With A Negative Charge;
It has a giant lattice structure with strong electrostatic forces of attraction. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study. Positively charged hydrogen atom, symbolized as h+. An) complete the following statements about ions.
(B) In A Colloid, Such As Milk, The Particles Are Much Larger But Remain Dispersed And Do Not Settle.
You will also be defining the terms, acids, bases, and salts. In an electrolyte, the electric current is carried by charged particles (ions) in solution. Hydrogen atom bonded to a water molecule, symbolized as h30+. When molten, however, it can conduct electricity because its ions.
At Any Given Time A Small Number Of Molecules In A Volume Of Water Are Separating Into Ions.
Plants obtain positively charged mineral ions from clay particles in the soil by cation exchange, in which (a) roots passively absorb the positively charged mineral ions (b) mineral ions flow freely along porous cell walls (c) roots secrete protons, which free other positively charged mineral ions. Web figure 11.29 (a) a solution is a homogeneous mixture that appears clear, such as the saltwater in this aquarium. In this section, we discuss the circular motion of the charged particle as well as other motion that results from a charged particle entering a magnetic field. Web learning outcomes define a solution and describe the parts of a solution.