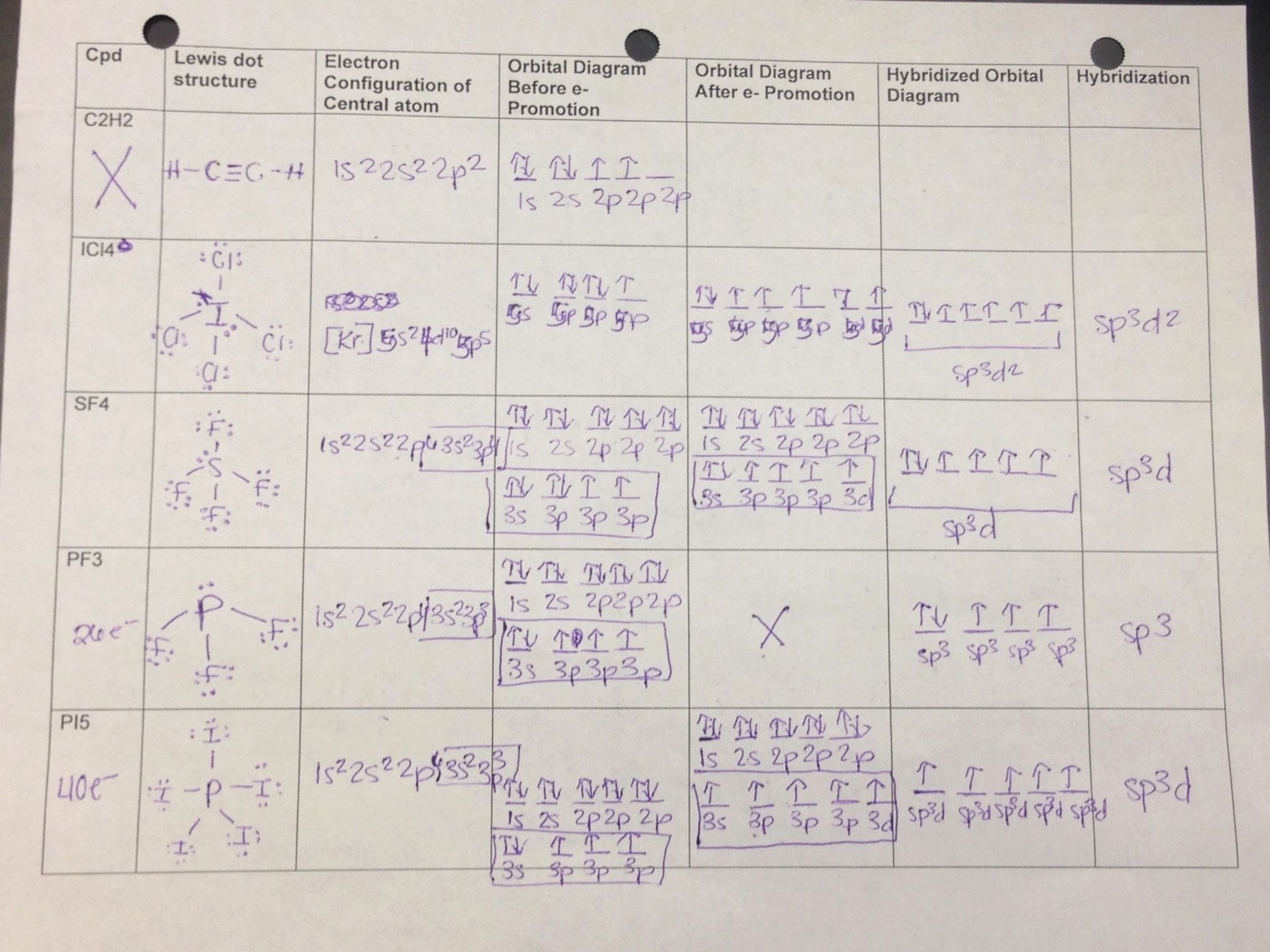
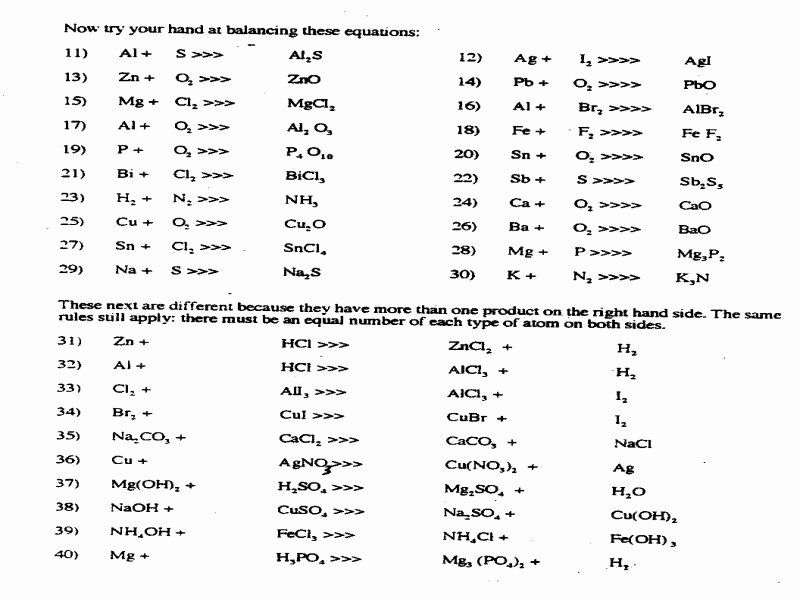
Chapter 18 Chemical Bonds Answer Key
Chapter 18 Chemical Bonds Answer Key - Web in the n 2 molecule, the nitrogen atoms have an σ bond and two π bonds holding the two atoms together. Covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how does a compound differ from its component elements?, what does a chemical formula represent?, how do electron dot diagrams help predict chemical bonding?. Click the card to flip 👆. What is the formula for. Web recognize stable electron configurations. A charge particle ionic bond: An ion is a _____ particle that has either more or fewer electrons than protons. Web ion a positively charged or negatively charged particle ionic bond a chemical bond between oppositely charged ions covalent bond a bond formed from shared electrons hydrate a crystalline substance that. The presence of three strong bonds makes n 2 a very stable molecule.
Compound names, element names, number and ratio of atoms • chemical bonds between atoms involve electrons • ionic bonds… A charge particle ionic bond: Web ion a positively charged or negatively charged particle ionic bond a chemical bond between oppositely charged ions covalent bond a bond formed from shared electrons hydrate a crystalline substance that. The instantaneous rate is the rate of a reaction at any particular point in time, a period of time that is so short that the concentrations of reactants and products change by a negligible amount. An ion is a _____ particle that has either more or fewer electrons than protons. • distinction between elements and compounds; Web recognize stable electron configurations. There are three types of bonds: Web chemical bonding is one of the most basic fundamentals of chemistry that explains other concepts such as molecules and reactions. When the highest occupied energy level of an atom is filled with electrons, the atom is stable.
7.1 the nature of chemical reactions by. Oxidation numbers are written as ______. Web 330 chapter 18 chemical bonds writing formulasyou have learned how to find oxidation numbers and their least common multiples. Click the card to flip 👆. The simplest example of bonding. What is the formula for. Without it, scientists wouldn't be able to explain why atoms are attracted to each other or how products are formed after a chemical. An atom’s ability to attract electrons ion: A _____ is the force of attraction between the opposite charges of the ions in an ionic compound. Click the card to flip 👆.
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonds
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how does a compound differ from its component elements?, what does a chemical formula represent?, how do electron dot diagrams help predict chemical bonding?. What is the formula for. Keep in mind that we are only dealing with the representative elements. A chemical bond created by the sharing of electrons.
30 Overview Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers Education Template
Bond energies and the enthalpy of reactions. Without it, scientists wouldn't be able to explain why atoms are attracted to each other or how products are formed after a chemical. Charged particle that has either more of fewer electrons than protons. When the highest occupied energy level of an atom is filled with electrons, the atom is stable. Web chapter.
And Potential Energy Worksheet Answers 9Th Grade Live
Web a molecule with strong bonds generally has less tendency to undergo chemical change than does one with weak bonds. Same elements may form different compounds • reading chemical formulas: Web in the n 2 molecule, the nitrogen atoms have an σ bond and two π bonds holding the two atoms together. 7.1 the nature of chemical reactions by. Web.
Section 1 Stability In Bonding Worksheet Answers Ivuyteq
Shows what elements a compounds contains and the exact number of the atoms of each element in a unit of that compound. Web chapter 18 section 2: Web a molecule with strong bonds generally has less tendency to undergo chemical change than does one with weak bonds. • distinction between elements and compounds; Without it, scientists wouldn't be able to.
30 Overview Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers Education Template
• distinction between elements and compounds; Web chapter 18 chemical bonds teaching resources | teachers pay teachers results for chapter 18 chemical bonds 18 results sort: An ion is a _____ particle that has either more or fewer electrons than protons. Keep in mind that we are only dealing with the representative elements. The ability to be drawn into wire.
50 Overview Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers Chessmuseum Template Library
Web chapter 18 chemical bonds review quiz for 9th grade students. What is the formula for. When the highest occupied energy level of an atom is filled with electrons, the atom is stable. The ability to be drawn into wire electronegativity: Web chapter 18 section 2:
Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answer Key
The ability to be drawn into wire electronegativity: Without it, scientists wouldn't be able to explain why atoms are attracted to each other or how products are formed after a chemical. Bond energies and the enthalpy of reactions. When the highest occupied energy level of an atom is filled with electrons, the atom is stable. Web a chemical bond is.
Student Exploration Ionic Bonds Answer Key Quizlet / Ionic Bonds Gizmo
Web chapter 18 section 2: Covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds and ionic bonds. A chemical bond created by the sharing of electrons ductility: Without it, scientists wouldn't be able to explain why atoms are attracted to each other or how products are formed after a chemical. The ability to be drawn into wire electronegativity:
Types Of Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers
Web 330 chapter 18 chemical bonds writing formulasyou have learned how to find oxidation numbers and their least common multiples. Compound names, element names, number and ratio of atoms • chemical bonds between atoms involve electrons • ionic bonds… Find other quizzes for science and more on quizizz for free! A chemical bond created by the sharing of electrons ductility:.
50 Chemical Bonding Worksheet Key Chessmuseum Template Library
Shows what elements a compounds contains and the exact number of the atoms of each element in a unit of that compound. Covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Web physical science chapter 18: • distinction between elements and compounds; Bond energies and the enthalpy of reactions.
7.1 The Nature Of Chemical Reactions By.
Web a molecule with strong bonds generally has less tendency to undergo chemical change than does one with weak bonds. Compound names, element names, number and ratio of atoms • chemical bonds between atoms involve electrons • ionic bonds… Charged particle that has either more of fewer electrons than protons. Bond energies and the enthalpy of reactions.
Web Chapter 18 Section 2:
The instantaneous rate is the rate of a reaction at any particular point in time, a period of time that is so short that the concentrations of reactants and products change by a negligible amount. The ability to be drawn into wire electronegativity: Covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Web recognize stable electron configurations.
Keep In Mind That We Are Only Dealing With The Representative Elements.
Web ion a positively charged or negatively charged particle ionic bond a chemical bond between oppositely charged ions covalent bond a bond formed from shared electrons hydrate a crystalline substance that. Same elements may form different compounds • reading chemical formulas: Click the card to flip 👆. Without it, scientists wouldn't be able to explain why atoms are attracted to each other or how products are formed after a chemical.
Web Physical Science Chapter 18:
Web chemical bonding is one of the most basic fundamentals of chemistry that explains other concepts such as molecules and reactions. When the highest occupied energy level of an atom is filled with electrons, the atom is stable. Web a chemical bond is formed when electrons are shared between two atoms. Web in the n 2 molecule, the nitrogen atoms have an σ bond and two π bonds holding the two atoms together.